Chapter 18 SNMP
GS-1524/GS-1548 User’s Guide
107
18.1.2 SNMP Traps
The Switch sends traps to an SNMP manager when an event occurs. SNMP traps
supported are outlined in the following table.
18.1.3 SNMP v3 and Authentication
SNMP v3 adds the concept of groups and users to enhance security for SNMP
management. A user is an SNMP manager. A group is a group of SNMP managers
that are assigned common access rights to MIBs. For example, one group of
managers may only have access to agents with MIB II - System Group MIBs while
another may have access to agents with the Ether-like MIB.
In addition, SNMP managers can also be required to authenticate with agents
before conducting SNMP management sessions.
Note: SNMP v3 is enabled when you create SNMP groups and users. Once SNMP v3
is enabled, you must configure unique SNMP communities for SNMP v1 and/or
SNMP v2c access.
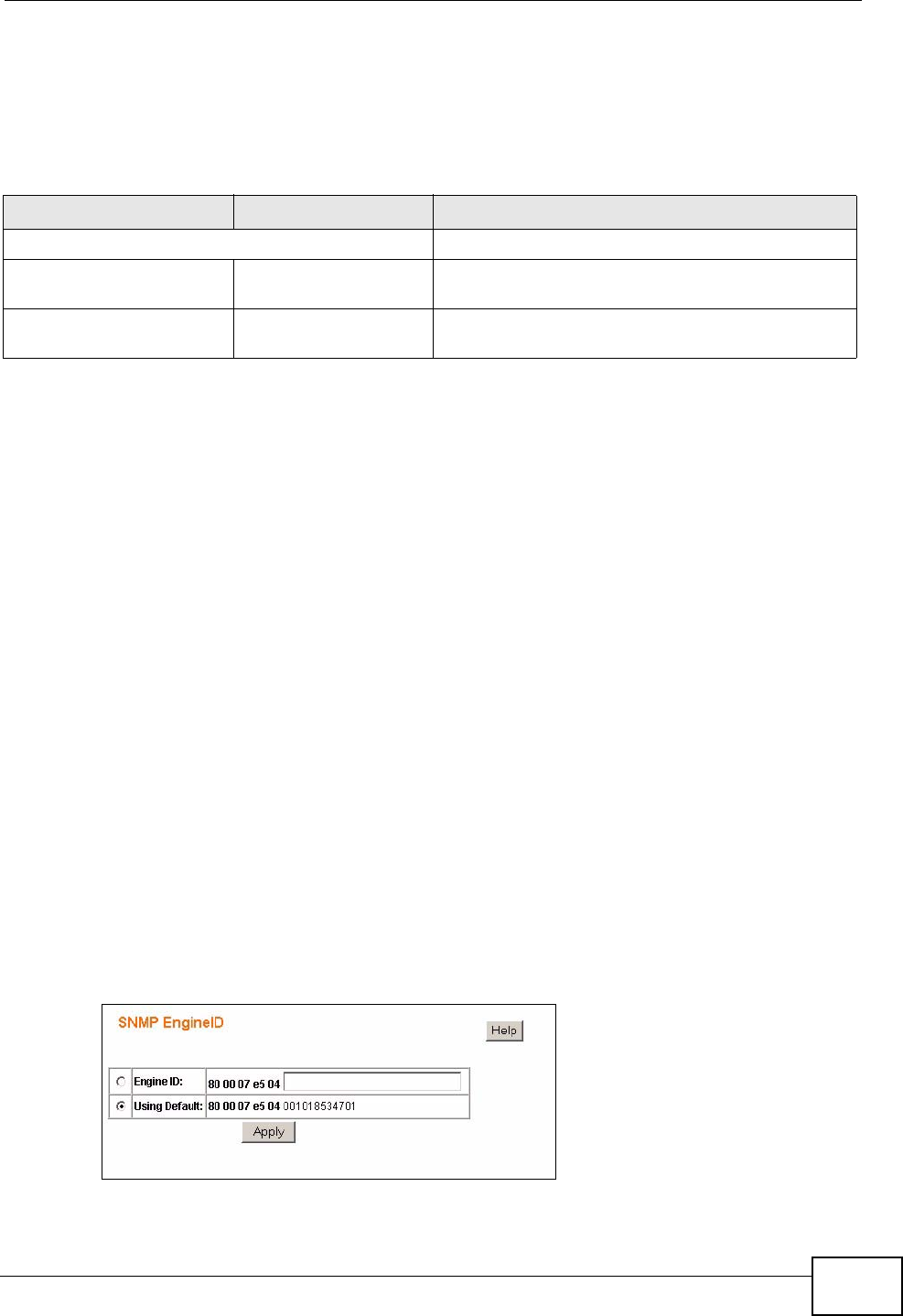
18.1.4 SNMP EngineID
The SNMP Engine ID is a unique identifier that identifies agents to the managers.
The default SNMP Engine ID is the MAC address of the agent. You can change this.
Use the SNMP EngineID screen to specify the Engine ID for the Switch.
Click SNMP > EngineID in the navigation panel to view the screen as shown.
Figure 60 SNMP EngineID
Table 39 SNMP Traps
OBJECT LABEL OBJECT ID DESCRIPTION
SNMPv1/SNMPv2 Trap/Inform Requests:
authenticationFailure 1.3.6.1.6.3.1.1.5.5 This trap is sent when an SNMP request comes
from non-authenticated hosts.
RFC2819 Traps
(alarmEntry)
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3.1.1 A RMON event has been triggered.
