19
If the arch slopes up – but not back down – then the front of the
transducer is too high and needs to be lowered. If only the back half of
the arch is printed, then the nose of the transducer is angled too far
down and needs to be raised.
NOTE:
Periodically wash the transducer's face with soap and water to
remove any oil film. Oil and dirt on the face will reduce the
sensitivity or may even prevent operation.
SHOOT-THRU-HULL PREPARATION
The transducer installation inside a fiberglass hull must be in an area
that does not have air bubbles in the resin or separated fiberglass
layers. The sonar signal must pass through solid fiberglass. A
successful transducer installation can be made on hulls with flotation
materials (such as plywood, balsa wood or foam) between layers of
fiberglass if the material is removed from the chosen area.
Epoxy the transducer to a solid portion of the hull.
For example, some (but not all) manufacturers use a layer of fiberglass,
then a core of balsa wood, finishing with an outer layer of fiberglass.
Removing the inner layer of fiberglass and the balsa wood core exposes
the outer layer of fiberglass. The transducer can then be epoxied
directly to the outer layer of fiberglass. After the epoxy cures, the hull
is watertight and structurally sound. Remember, the sonar signal must
pass through solid fiberglass. Any air bubbles in the fiberglass or the
epoxy will reduce or eliminate the sonar signals.
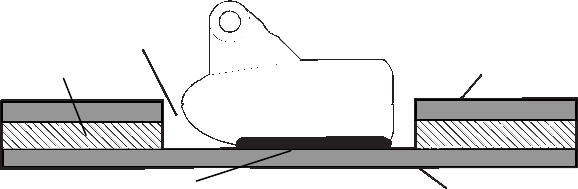
Fill with polyester resin
Inner hull
Epoxy to hull first
Outer hull
Flotation material


















