2-1
2. DESCRIPTION OF RADAR
2.1 General
2.1.1 Minimum and maximum ranges
Minimum range
The minimum range is defined by the shortest distance at which, using a scale of
0.0625 or 0.125 nm, a target that has an echoing area of 10 m
2
is shown separate from
the point that shows the antenna position.
The minimum range depends on the pulselength, antenna height, and signal process-
ing (like main bang suppression and digital quantization). Use a shorter range scale
as far as it gives favorable definition or clarity of picture.
The FR-8045/FR-8065/FR-8125/FR-8255 radar series meets the requirements of
IEC 62252 5.14.1 (Class A).
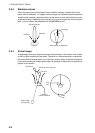
Maximum range
The maximum detection range, Rmax, changes depending on the height of the anten-
na, the height of the target above the sea, the size, shape and material of the target,
and the atmospheric conditions.
Under normal atmospheric conditions, the maximum range is equal or a little shorter
than the optical horizon. The radar horizon is longer than the optical one by approxi-
mately 6%, because of the diffraction property of the radar signal. The Rmax is shown
in the following formula.
If the height of the antenna is 9 m and the height of the target is 16 m, the maximum
radar range is;
Note: The detection range is reduced by any precipitation (which absorbs the radar
signal).
R
max
= 2.2 x ( h1 + h2)
where R
max
: radar horizon (nautical miles)
h1: antenna height (m)
h2: target height (m)
Radar horizon
Optical horizon
R
max
= 2.2 x ( 9 + 16) = 2.2 x (3 + 4) = 15.4 nm