%$6,&&20081,&$7,216
22
$075$160,66,21
Each mode used on the HF Amateur bands has its
own advantages. Although long distance DX contacts
may be less common while using AM, the superior
audio quality characteristic of AM operation is one
reason why some hams prefer this mode.
If necessary, refer to “OPERATING BASICS”,
beginning on page 10, for details on how to receive.
1 Select an operating frequency.
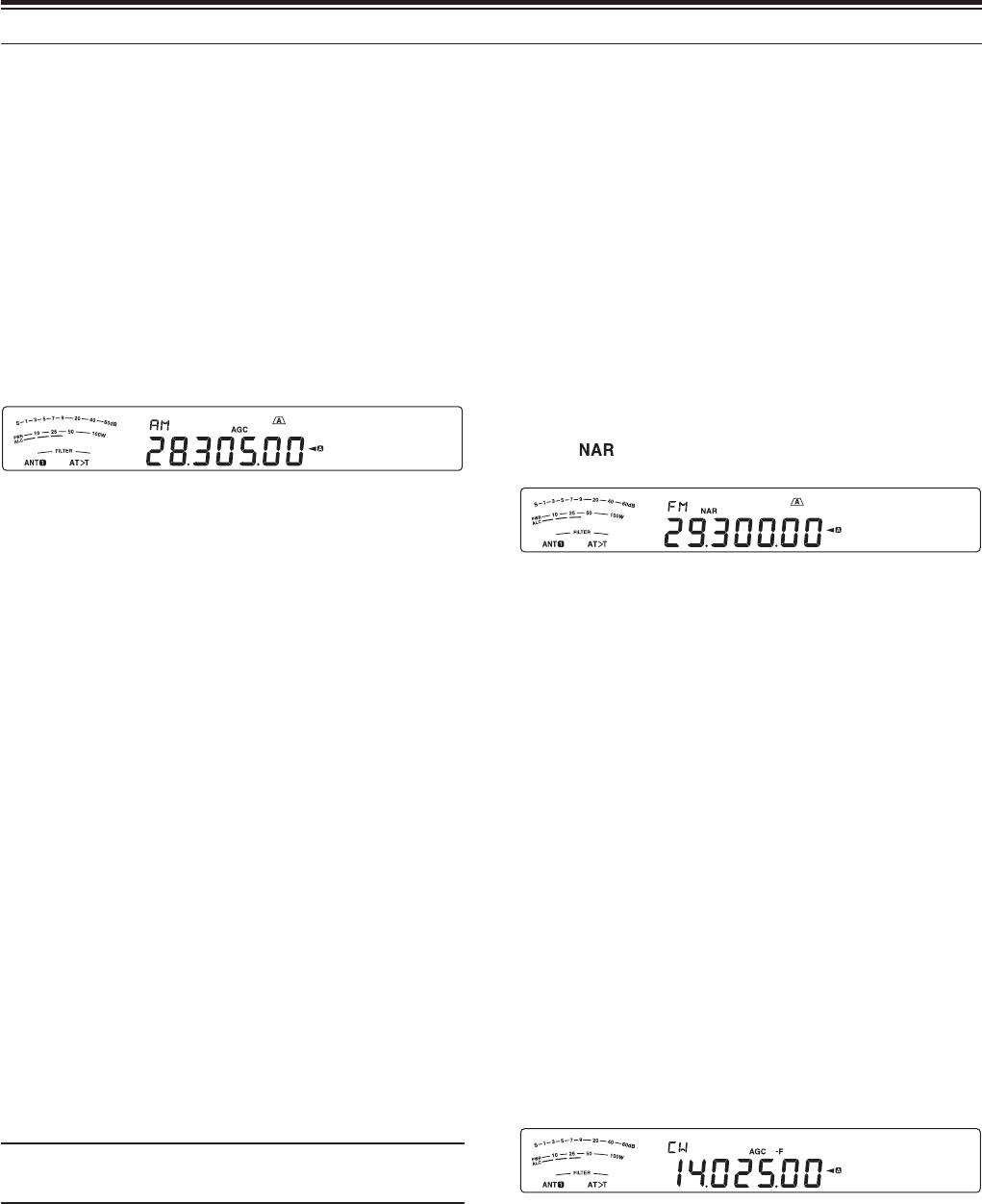
2 Press [FM/AM (FM-N)] until “AM” appears.
• If “AM” does not appear, select “FM” first, then
press [FM/AM (FM-N)]. The mode indicator
changes to “AM”.
3 Press [MIC (CAR)] to enter the Microphone gain
adjustment mode.
• The current gain level appears on the sub-
display.
4 Press and hold Mic [PTT].
• The TX-RX LED lights red.
• Refer to “VOX” {page 30} for information on
automatic TX/ RX switching.
5 Speak into the microphone and adjust the
MULTI/CH control so that the power meter slightly
reflects your voice level.
• Speak in your normal tone and level of voice.
Speaking too close to the microphone or too
loudly may increase distortion and reduce
intelligibility at the receiving end.
• You may want to use the Speech Processor.
Refer to “SPEECH PROCESSOR” {page 31}
for details.
6 Release Mic [PTT] to return to Reception mode.
• The TX-RX LED lights green or turns off,
depending on the SQL control position.
7 Press [MIC (CAR)] or [CLR] to exit the Microphone
gain adjustment mode.
Refer to “COMMUNICATING AIDS”, beginning on
page 28, for information on additional useful operation
functions.
Note: When the TX power meter reading exceeds the value that
you specified in the TX Power setting {page 56}, decrease the
microphone gain or adjust your tone and level of voice.
1$552:%$1':,'7+)25)0
Select wide band or narrow band TX deviation
depending on whether the other station is using wide
band or narrow band filter for FM mode. While “NAR”
appears, the TS-590S transceiver transmits signals in
narrow band FM but the reception IF filter bandwidth
remains unchanged (Wide). The deviation selection
is crucial to avoid audio distortion or insufficient
intelligibility that the other station will encounter.
1 Press [FM/AM (FM-N)] until “FM” appears.
•
If “FM” does not appear, select “AM” first, then
press [FM/AM (FM-N)].
The mode indicator
changes to “FM”.
2 Press and hold [FM/AM (FM-N)] to toggle the
selection between wide and narrow TX deviation.
•“
” appears when narrow TX deviation is
selected.
&:75$160,66,21
CW operators know that this mode is very reliable
when communicating under worst conditions. It may
be true that newer digital modes rival CW as being
equally as useful in poor conditions. These modes,
however, do not have the long history of service nor
the simplicity that CW provides.
This transceiver has a built-in electronic keyer that
supports a variety of functions. For details on using
these functions, refer to “ELECTRONIC KEYER”
{page 33}.
If necessary, refer to “OPERATING BASICS”,
beginning on page 10, for details on how to receive.
1 Select the operating frequency.
2 Press [CW/FSK (REV)] until “CW” appears.
• If “CW” does not appear, select “FSK” first, then
press [CW/FSK (REV)]. The mode indicator
changes to “CW”.
• To precisely tune in another station, use Auto
Zero-beat. Refer to “AUTO ZERO-BEAT”
{page 23}.
3 Press [SEND].
• The TX-RX LED lights red.
4 Operate the Keys or Paddle.
• As you transmit, you should hear a sidetone
that lets you monitor your own transmission.
5 Press [SEND] to return to Reception mode.
• The TX-RX LED lights green or turns off,
depending on the SQL control setting.