5 Reference
Design
HP delivers content as "features," each of which is a self-contained set of files and jobs. Each
feature is independent, and resides in its own folder with key files located in the root folder and
other supporting files located in various subfolders.
Because the features are independent, their jobs are also independent. That means there are no
monolithic jobs that configure the system, configure the smart array, install an operating system
and install a support pack. Jobs are solely in a toolbox scheme. Servers auto-configure themselves,
so default hardware configuration jobs are not necessary. If needed, hardware configuration jobs
will have to be scheduled before operating system jobs. There are a few exceptions to this scheme,
such as jobs that deploy a virtualization host include a system configuration task to enable the
processor virtualization extensions.
Operating system feature naming consists of four elements — os+version, architecture,
edition, and language/locale — that appear in some combination between the feature’s
folder name and the answer file names. There are a few exceptions to this scheme, such as operating
systems that do not include the concept of editions. Operating system features map one-to-one with
their media. For example, for Windows Server 2008 Enterprise (X64) English, the folder name is
ws6-x64-en_us and the unattend answer files are unattend-ent.xml and
unattend-std.xml. There is one media consisting of multiple editions.
The provided jobs and files are sufficient for generic operating system deployment. For more
complex deployments, you can use the provided jobs and files as templates. When this is the case,
HP strongly recommends that you follow a copy, rename, and modify process — copy the job or
file, rename it so that the name conveys the new behavior, and make the necessary modifications.
This process provides a clean separation between the customized jobs and the provided jobs and
enables the provided jobs to act as working baselines.
NOTE: When editing ESX or Linux files on the Deployment Server, use a text editor that saves
the file in Linux compatible format.
NOTE: When editing Windows 2008 answer files, use the Windows System Image Manager
utility included in the Windows Automated Installation Kit (AIK).
NOTE: Server Deployment program files inherit file and folder permissions from their parent
folder. Express share needs a minimum of read permission to allow all users to download and to
execute the task.
Firmware and hardware features
These features enable you to flash the firmware, read/write system configuration, read/write smart
array configuration, and read/write fiber channel host bus adapter configuration.
• Jobs denoted with server-specific use an input or output filename based on the computer
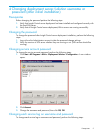
ID of the target server instead of a static filename. To determine the computer ID, in the
Deployment Console, right-click on the computer and select Properties.
• To determine the filename of the input or output file, look for the inputfilename or
outputfilename variable in the relevant Run Script task.
• When executing a read job, the output file will be overwritten.
12 Reference