77
Explanation
L
v
TΔuv
Following factors can be acquired as measurement value with L
v
TΔuv as color space of this instrument.
L
v
: Luminance
T :Correlated color temperature
Δuv :Color difference from blackbody locus
While L
vs
stands for luminance, T and Δuv for color in L
v
TΔuv.
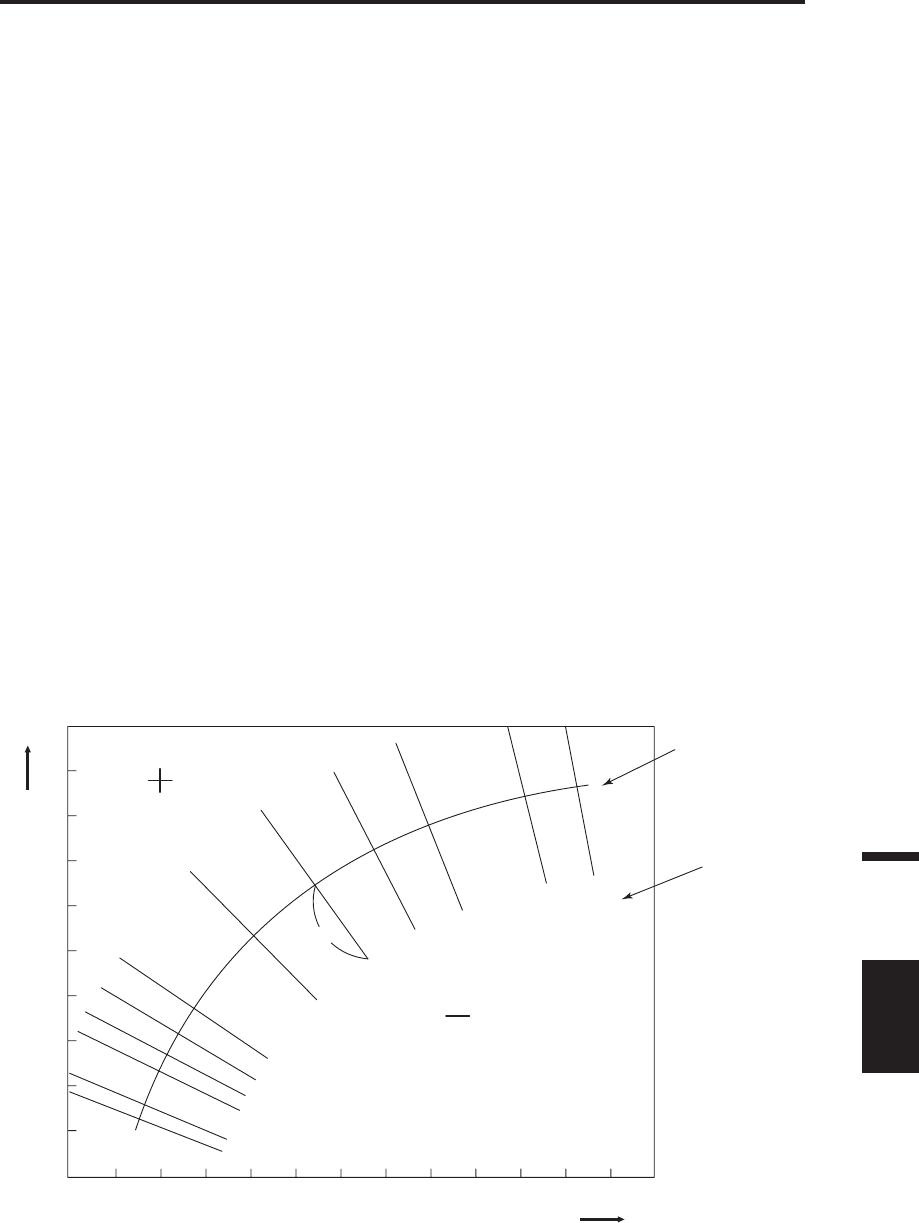
<Relation between correlated color temperature T and color difference from blackbody locus Δuv>
Color temperature refers to the temperature of black body (perfect radiator) which has
equal chromaticity coordinates to certain light. However, color temperature only represents
colors on blackbody locus.
Correlated color temperature, slightly wider interpretation of color temperature, is very
useful to eliminate such problem. Here, correlated color temperature covers those which
are slightly outside the range of that of blackbody locus.
If a certain color positions on isotemperature line, the intersection point of isotemperature
line and blackbody locus is indicated as correlated color temperature for the color.
Isotemperature line means line on chromaticity coordinates which is a set of colors visually
close to color temperature on blackbody locus.
However, since all colors on a color-matching temperature line are represented with equal
correlated color temperature, it is not possible to describe color only with correlated color
temperature. To solve that, Δuv, deviation of correlated color temperature T from
blackbody locus, is to apply for that purpose.
If Δuv exists above blackbody locus, it is represented with “+”, and below, with “-”.
v
u
Blackbody locus
Correlated
temperature T
Correlated temperature T and Δuv
13000K
5000K
3000K
2300K
Δuv
0.35
0.30
0.20
0.25
0.30
