Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling and SDT Connector
724-746-5500 | blackbox.com
57
RealVNC http://www.realvnc.com is fully cross-platform, so a desktop running on a Linux
machine may be displayed on a Windows PC, on a Solaris machine, or on any number of
other architectures. There is a Windows server, allowing you to view the desktop of a remote
Windows machine on any of these platforms using exactly the same viewer. RealVNC was
founded by members of the AT&T team who originally developed VNC.
TightVNC http://www.tightvnc.com is an enhanced version of VNC. It has added features such
as file transfer, performance improvements, and read-only password support. They have just
recently included a video drive much like UltraVNC. TightVNC is still free, cross-platform
(Windows Unix, and Linux), and compatible with the standard (Real) VNC.
UltraVNC http://ultravnc.com is easy to use, fast, and free VNC software that has pioneered
and perfected features that the other flavors have consistently refused or been very slow to
implement for cross platform and minimalist reasons. UltraVNC runs under Windows
operating systems (95, 98, Me, NT4, 2000, XP, 2003). Download UltraVNC from
Sourceforge's UltraVNC file list.
For Linux servers (and clients):
Most Linux distributions now include VNC Servers and Viewers and they generally can be launched from the (Gnome/KDE etc) front end; for
example, with Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4 there’s VNC Server software and a choice of Viewer client software, and to launch:
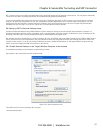
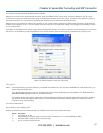
Select the Remote Desktop entry in the Main Menu -> Preferences menu.
Click the Allow other users… checkbox to allow remote users to view and control your desktop.
Figure 6-27. Remote Desktop Preferences screen.
To set up a persistent VNC server on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4:
• Set a password using vncpasswd
• Edit /etc/sysconfig/vncservers
• Enable the service with chkconfig vncserver on
• Start the service with service vncserver start