289
Useful functions
4
PARAMETERS
4.22.6 Initiating a fault (Pr.997)
...............Specifications differ according to the date assembled. Refer to page 378 to check the SERIAL number.
The above parameters can be set when User group read selection="0." (Refer to page 201)
* This parameter allows its setting to be changed during operation in any operation mode even if "0 (initial value) or 1" is set in Pr. 77 Parameter write
selection.
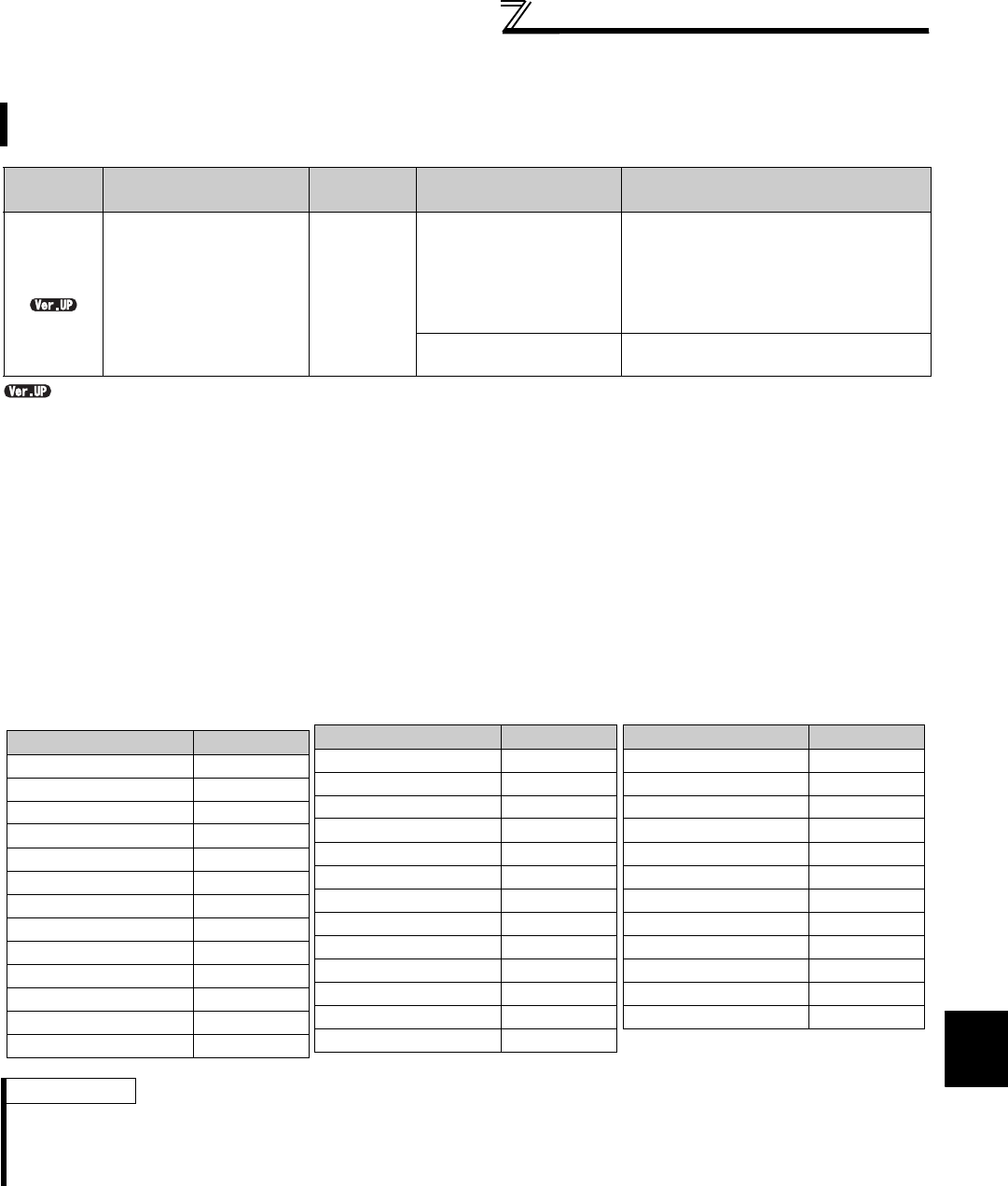
(1) Fault initiation (Pr. 997)
⋅ To initiate a fault, set the assigned number of the fault you want to initiate in Pr. 997 Fault initiation.
⋅ The value set in Pr. 997 Fault initiation is not stored in EEPROM.
⋅ When a fault occurs, the inverter trips, and the fault is displayed and output (ALM, ALM2).
⋅ While the initiated fault is occurring, the fault is displayed as the latest fault in the faults history. After a reset, the
faults history goes back to the previous status. (The fault generated by the fault initiation function is not saved in the
faults history.)
⋅ Perform inverter reset to cancel the fault.
Setting for Pr. 997 Fault initiation and corresponding faults
A fault is initiated by setting the parameter.
This function is useful to check how the system operates at a fault.
Parameter
number
Name Initial value Setting range Description
997 *
Fault initiation 9999
16 to 18, 32 to 34, 48, 49,
64, 80 to 82, 96, 97, 112,
128, 129, 144, 145, 160,
161, 176 to 179,
192 to 194, 196 to 199,
230, 241, 245 to 247, 253
The setting range is same with the one for
fault data codes of the inverter (which can
be read through communication).
Written data is not stored in EEPROM.
When "0" is set, nothing happens.
9999
The read value is always "9999."
This setting does not initiate a fault.
REMARKS
⋅ If a fault is already occurring in the inverter, a fault cannot be initiated by Pr. 997.
⋅ The retry function is invalid for the fault initiated by the fault initiation function.
⋅ If another fault occurs after a fault has been initiated, the fault indication does not change.
The fault is not saved in the faults history either.
Setting (Data code) Fault
16(H10) OC1
17(H11) OC2
18(H12) OC3
32(H20) OV1
33(H21) OV2
34(H22) OV3
48(H30) THT
49(H31) THM
64(H40) FIN
80(H50) IPF
81(H51) UVT
82(H52) ILF
96(H60) OLT
97(H61) SOT
112(H70) BE
128(H80) GF
129(H81) LF
144(H90) OHT
145(H91) PTC
160(HA0) OPT
161(HA1) OP1
176(HB0) PE
177(HB1) PUE
178(HB2) RET
179(HB3) PE2
192(HC0) CPU
Setting (Data code) Fault
193(HC1) CTE
194(HC2) P24
196(HC4) CDO
197(HC5) IOH
198(HC6) SER
199(HC7) AIE
230(HE6) PID
241(HF1) E.1
245(HF5) E.5
246(HF6) E.6
247(HF7) E.7
253(HFD) E.13
Setting (Data code) Fault


















