Chapter 2 Hardware Overview
NI 5911 User Manual 2-2
©
National Instruments Corporation
Measurement Fundamentals
The NI 5911 has a differential programmable gain input amplifier (PGIA)
at the analog input. The purpose of the PGIA is to accurately interface to
and scale the signal presented at the connector to the analog-to-digital
converter (ADC) regardless of source impedance, source amplitude, DC
biasing or common-mode noise voltages.
Differential Input
When measuring high dynamic range signals, ground noise is often a
problem. The PGIA of the NI 5911 allows you to make noise-free
measurements of the signal. The NI 5911 PGIA is a differential amplifier.
The PGIA differential amplifier efficiently rejects any noise which may be
present on the ground signal. Internal to the PGIA, the signal presented at
the negative input is subtracted from the signal presented at the positive
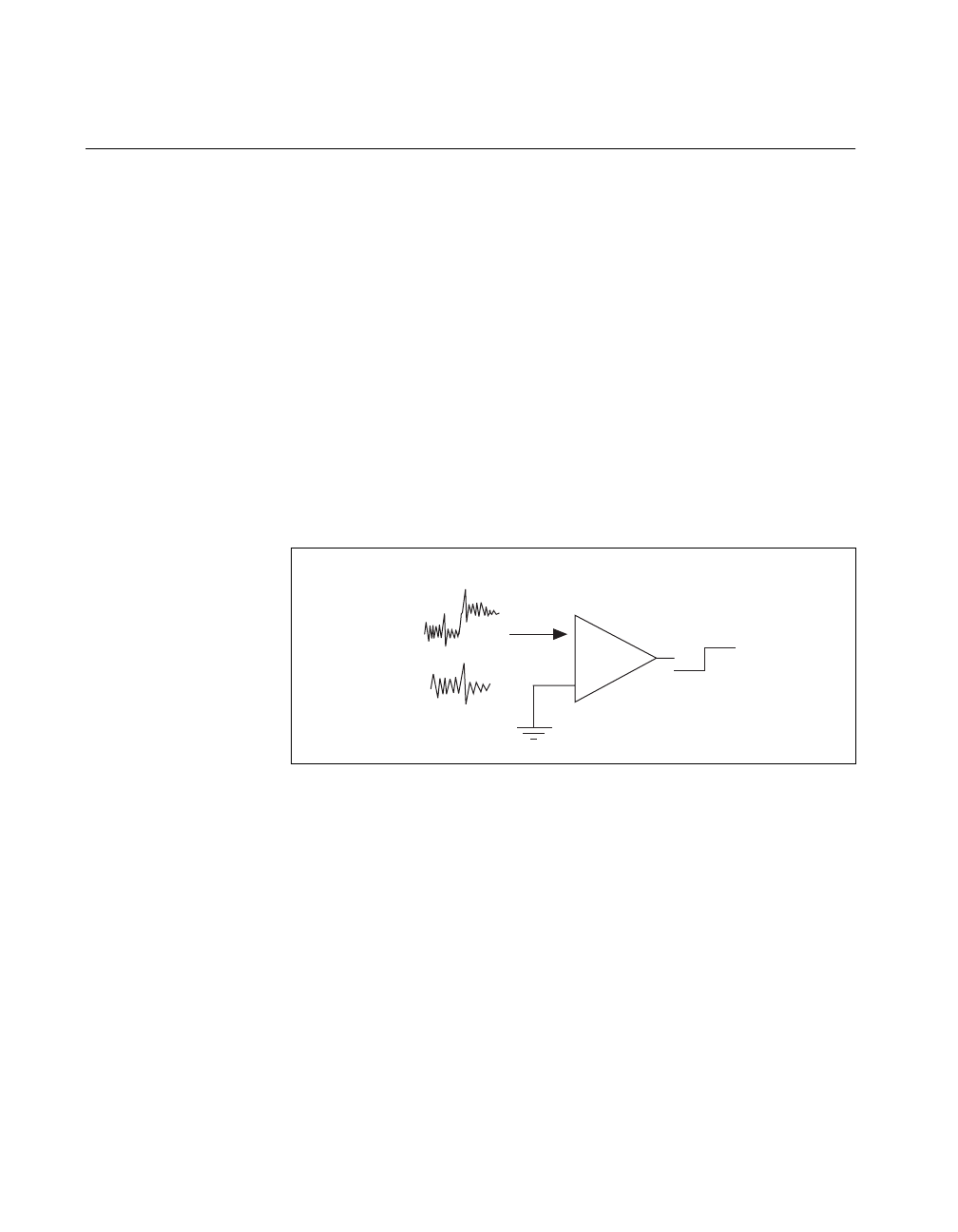
input. As shown in Figure 2-2, this subtraction removes ground noise from
the signal. The inner conductor of the BNC is V+, the outer shell is V–.
Figure 2-2.
Noise-Free Measurements of Signal
Grounding Considerations
The path for the positive signal has been optimized for speed and linearity.
You should always apply signals to the positive input and ground to the
negative input. Reversing the inputs will result in higher distortion and
lower bandwidth.
The negative input of the amplifier is grounded to PC ground through a
10 kΩ resistor. The PGIA is therefore referenced to ground, so it is not
necessary to make any external ground connections. If the device you
connect to the NI 5911 is already connected to ground, ground-loop noise
voltages may be induced into your system. Note that in most of these
situations, the 10 kΩ resistance to PC ground is normally much higher than
+
–
V
out
V+
Input Signal
Ground Noise
V–
CBIHWum.book Page 2 Thursday, October 29, 1998 1:56 PM