Chapter 12 IPSec VPN
P-2812HNU-51c User’s Guide
274
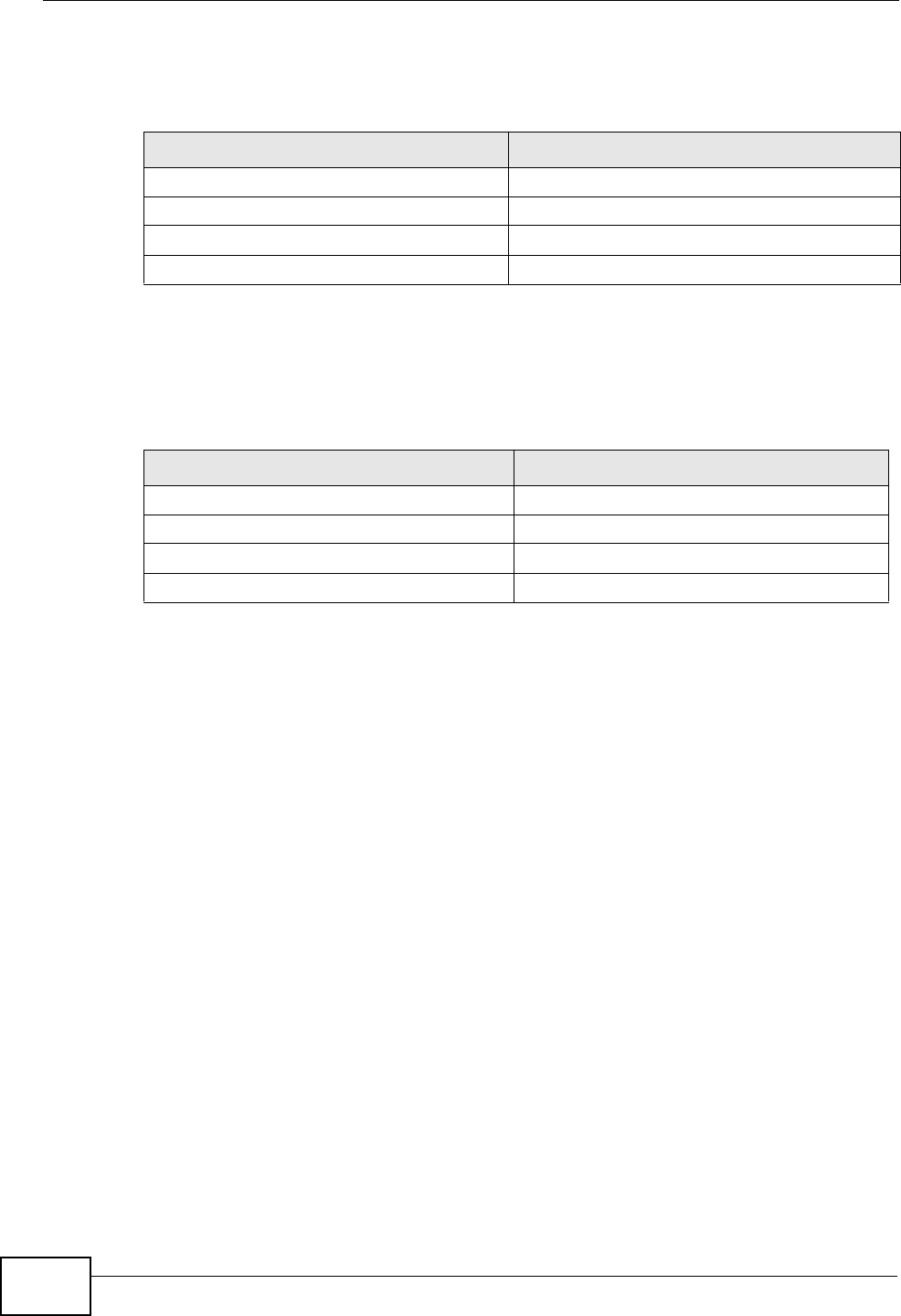
The two P-2812HNU-51cs in this example can complete negotiation and establish
a VPN tunnel.
The two P-2812HNU-51cs in this example cannot complete their negotiation
because P-2812HNU-51c B’s Local ID type is IP, but P-2812HNU-51c A’s
Remote ID type is set to E-mail. An “ID mismatched” message displays in the
IPSEC LOG.
12.5.8 Pre-Shared Key
A pre-shared key identifies a communicating party during a phase 1 IKE
negotiation (see Section 12.5.3 on page 269 for more on IKE phases). It is called
“pre-shared” because you have to share it with another party before you can
communicate with them over a secure connection.
12.5.9 Diffie-Hellman (DH) Key Groups
Diffie-Hellman (DH) is a public-key cryptography protocol that allows two parties
to establish a shared secret over an unsecured communications channel. Diffie-
Hellman is used within IKE SA setup to establish session keys. 768-bit, 1024-bit
1536-bit, 2048-bit, and 3072-bit Diffie-Hellman groups are supported. Upon
completion of the Diffie-Hellman exchange, the two peers have a shared secret,
but the IKE SA is not authenticated. For authentication, use pre-shared keys.
Table 81 Matching ID Type and Content Configuration Example
P-2812HNU-51C A P-2812HNU-51C B
Local ID type: E-mail Local ID type: IP
Local ID content: tom@yourcompany.com Local ID content: 1.1.1.2
Remote ID type: IP Remote ID type: E-mail
Remote ID content: 1.1.1.2 Remote ID content: tom@yourcompany.com
Table 82 Mismatching ID Type and Content Configuration Example
P-2812HNU-51C A P-2812HNU-51C B
Local ID type: IP Local ID type: IP
Local ID content: 1.1.1.10 Local ID content: 1.1.1.2
Remote ID type: E-mail Remote ID type: IP
Remote ID content: aa@yahoo.com Remote ID content: 1.1.1.0
