- 52 -
4.1 PRECAUTIONS FOR SELECTING PERIPHERAL DEVICES
4.1.1 Measures against noises
In this section, noises indicate those of more than 40th to 50th high frequencies in a power distribution
system, which assume generally irregular conditions.
Some noises enter the high power factor converter to adversely affect it and others are radiated by the high
power factor converter to adversely affect peripheral devices. Though the high power factor converter is
designed to be immune to noises, it handles low-level signals, so it requires the following basic measures to
be taken. Also, since the high power factor converter chops output voltage at high carrier frequency, it could
generate noises. If these noises affect peripheral devices, measures should be taken to suppress noises.
The measures differ slightly depending on noise propagation paths.
1) Basic measures
• Do not run the power cables (I/O cables) and signal cables of the high power factor converter in parallel with each
other and do not bundle them.
• Use twisted shield cables for the detector connecting and control signal cables and connect the screen of the shield
cables to terminal SD.
• Ground the reactors 1, 2, external box, high power factor converter, inverter, motor, etc. at one point.
2) Measures against noises which enter and affect the high power factor converter
When devices which generate many noises (which use magnetic contactors, magnetic brakes, many relays, for
example) are installed near the high power factor converter and the high power factor converter may be affected by
noises, the following measures must be taken:
• Provide surge suppressors for devices that generate many noises to suppress noises.
• Fit data line filters to signal cables.
• Ground the shields of the detector connection and control signal cables with a metal cable clamp.
3) Measures against noises which are radiated by the high power factor converter to affect peripheral
devices
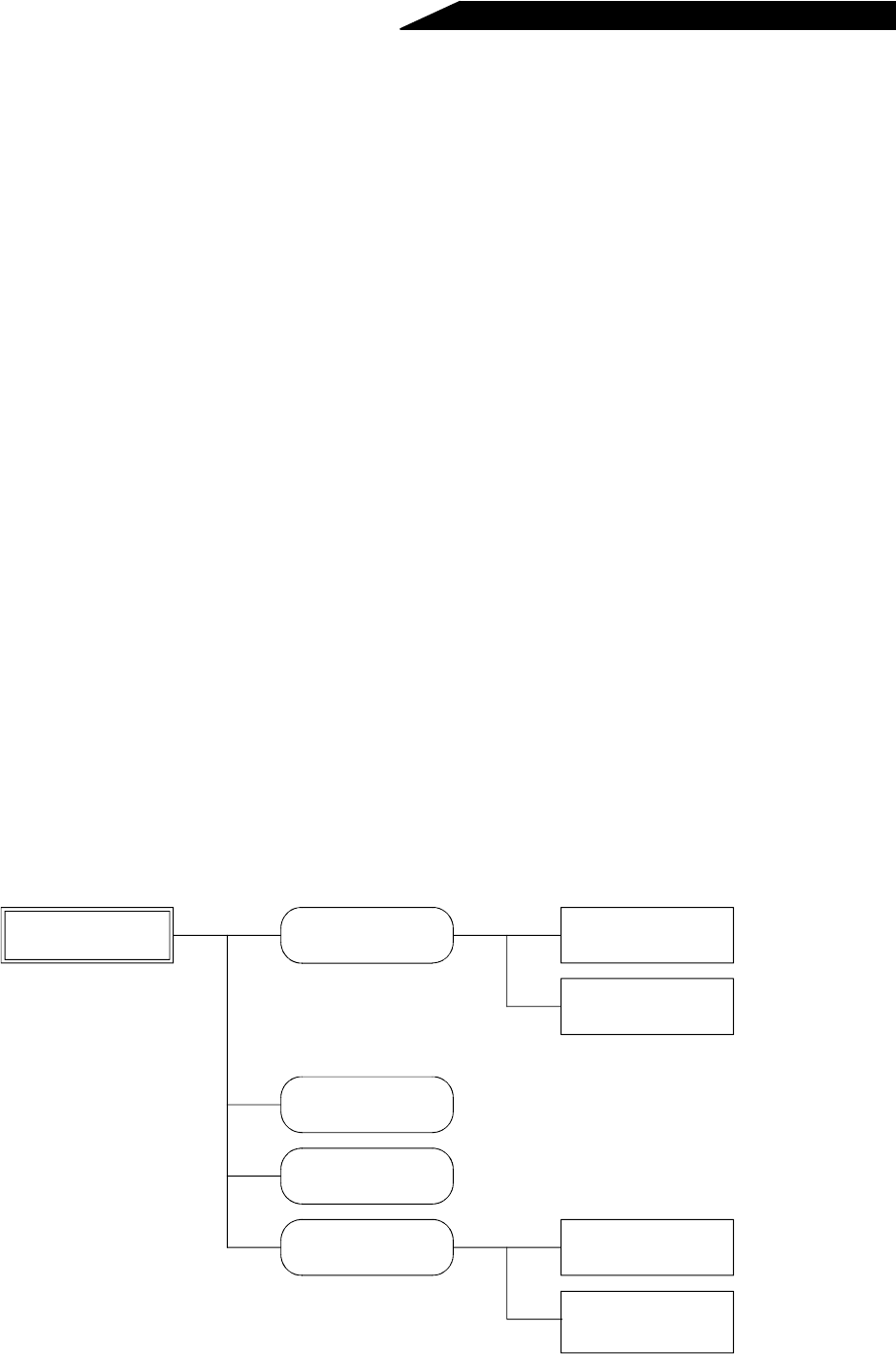
Noises generated by the high power factor converter are largely classified into those radiated by the cables connected
to the high power factor converter and high power factor converter’s main circuit (I/O), those electromagnetically and
electrostatically inducted to the signal cables of the peripheral devices close to the main circuit power supply, and
those transmitted through the power supply cables.
Converter-generated
noises
Air-propagated noises
Noises directly
radiated by converter
Noises radiated
by power cables
Magnetic induction
noises
Static induction noises
Cable-propagated
noises
.. Path 4, 5
Noises propagated
through power cables
Sneak noises from
ground cable due to
leakage current
.. Path 6
.. Path 1
.. Path 2
.. Path 7
.. Path 8