LM10 MOTOR PROTECTION SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 4–25
LM10 Motor Protection System
Chapter 4: Functionality
GE Consumer & Industrial
Multilin
Functional ity
4.1 Overcurrent Fault Conditions
4.1.1 Descriptions
When current for any of the three phases becomes greater than the nominal full load
current (FLA), the unit calculates time to trip. The FLA, trip class, CT ratio and number of
passes/turns through the CT, and current input readings are taken into account. Separate
algorithms are used for “cold” and “hot” motors. Since the LM10 does not measure
temperature directly, motor condition is extrapolated from operating current versus the
FLA setting.
The FLA value can be set from 1.2 to 800 A in steps of 0.1. This fault value is monitored
continuously and can not be disabled.
The motor “hot” condition is determined based a variable algorithm. Once a fault condition
is reached, the unit may not be Reset until an appropriate cool-down period has elapsed.
This is once again calculated based on FLA, trip class, CT ratio and number of passes/turns
through the CT, and current input readings.
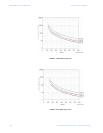
The time to trip is a function of percent overcurrent, trip class, and motor condition (cold or
hot). The current level must exceed 1.2 × FLA for the trip timeout to run. This time is
cumulative and will not time in unless the level drops below 1.0 × FLA.
A class 10 motor has the shortest trip times while a class 30 has the longest. The trip class
should be selected based on motor size and type (see Switches on page 1–4 for details on
setting the trip class).
The LM10 monitors average current of the three phases over time to determine the motor
condition.