3-13
Measurements Applications
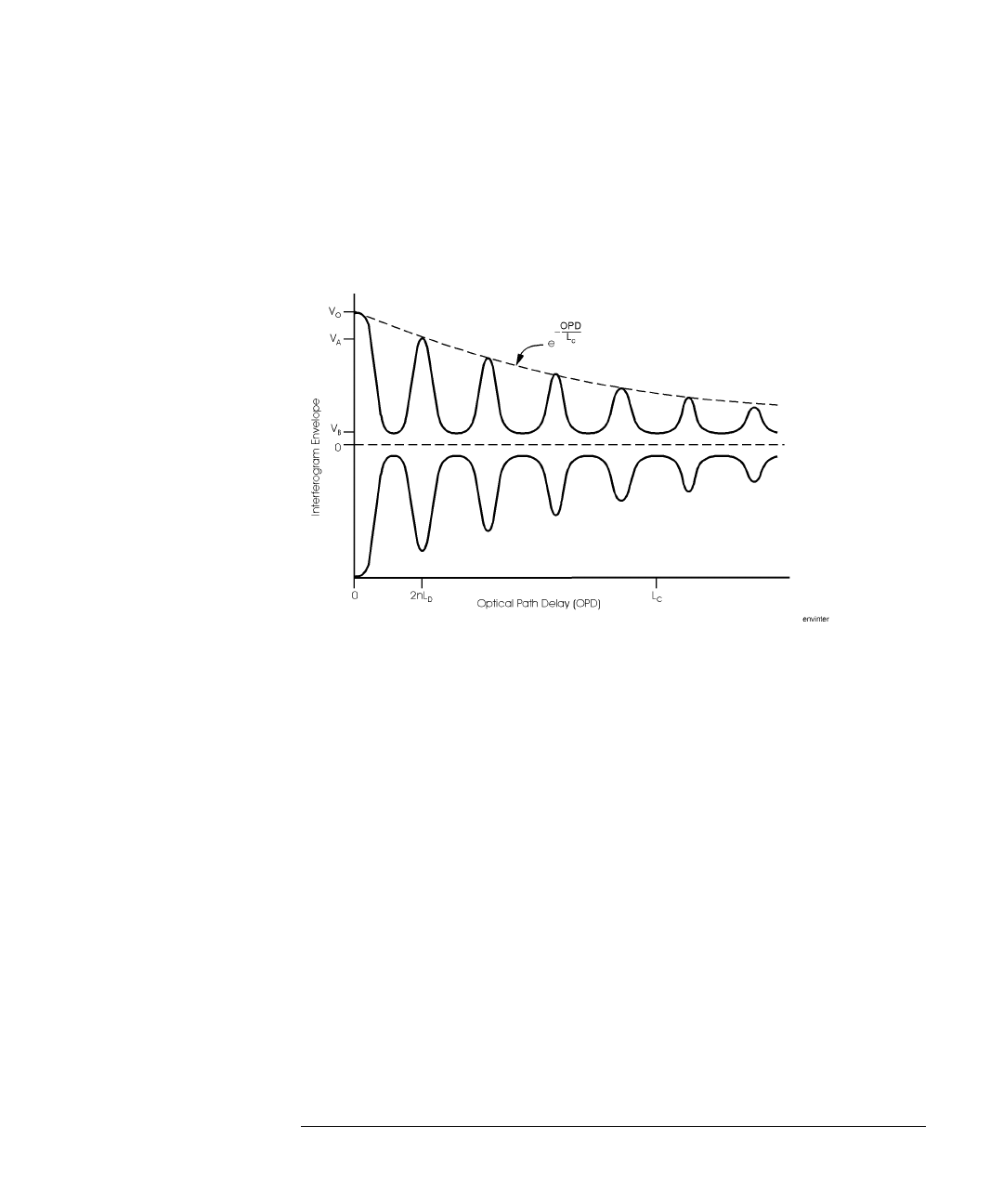
Measuring Coherence Length
Coherence length
(L
c
)
The interferogram of the laser being tested is sampled and the envelope of the
interferogram is found. This envelope has peaks (regions of high fringe visibil-
ity) at zero optical path delay and at delays equal to multiples of the laser cav-
ity round-trip optical length. This is shown in the following figure of the
interferogram envelope:
The amplitudes of the peaks decreases exponentially from the largest peak at
zero path delay. The exponential decay constant is defined as the coherence
length, Lc. The curve that connects the tops of the envelope peaks is given by
the following equation:
OPD is the optical path delay and Lc is the coherence length. Thus, at an opti-
cal path delay equal to the coherence length, the envelope peaks are down to
of their value at zero path delay peak. All envelope peaks found are used
to determine the exponential decay constant (coherence length) using a least
squares fit.
Round trip optical
length of diode
laser cavity
(2nLd)
The average optical path delay spacing of the envelope peaks is measured.
This is equal to the diode laser cavity round trip optical length, 2nLd.
decay curve
e
OPD
L
c
------------–
=
1
e
⁄


















