HP E1312A/E1412A Multimeter Application Information 53Chapter 2
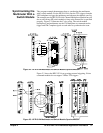
Hardware Used 486 IBM compatible computer running Windows 3.1. The computer has an
HP 82341 HP-IB interface and HP SICL/Windows 3.1 and Windows NT
for HP-IB software. The VXI modules were loaded in a VXI C-size
mainframe using an HP E1406A or B-size mainframe with HP E1306A
Command Module as resource manager connected to the computer via the
HP 82341 HP-IB card.
Making Multimeter
Measurements
This section provides four programs that demonstrate different ways of
making measurements and retrieving the readings. SCPI command
sequences for each program are contained in the boxes. The four programs:
1. Use the
MEASure command to make a single measurement.
2. Make several externally triggered measurements.
3. Maximize measurement speed on multiple measurements.
4. Maximize measurement accuracy on multiple measurements.
NOTE: Review the section titled “Triggering the Multimeter” beginning on
page 45 to fully understand the triggering system.
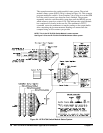
MEASure Command The simplest measurement method is using the MEASure command which
configures the function to be measured, initiates the measurement(s) and
places the reading(s) directly into the output buffer. You then must provide
the I/O construct to retrieve the readings and enter them into the computer.
One
MEASure command will initiate multiple measurements if the trigger
count or the sample count is greater than 1. The measurement process stops
when the output buffer fills if readings are not retrieved fast enough. The
measurement process restarts when there is again room to store readings in the
output buffer.
READ? Command The READ? command requires that you configure the multimeter for the
function you want to measure prior to issuing the command. The command
initiates the measurement(s) and places the reading(s) directly into the output
buffer like the
MEASure command. You then must provide the I/O construct
to retrieve the readings and enter them into the computer. One
READ?
command will initiate multiple measurements if the trigger count or the
sample count is greater than 1. The measurement process stops when the
output buffer fills if readings are not retrieved fast enough. The measurement
process restarts when there is room to store readings in the output buffer.
INIT and FETC?
Commands
The READ? command is broken down into two operations with the INIT and
FETC? commands. The INIT and FETC? commands require that you
configure the multimeter for the function you want to measure prior to
issuing the commands. The
INIT command initiates the measurement(s) and
places the reading(s) into the multimeter's RAM memory. This memory will
hold a maximum of 512 readings. You use the
FETC? command to transfer
the readings from memory to the output buffer. You then must provide the
I/O construct to retrieve the readings and enter them into the computer. One
INIT command will initiate multiple measurements if the trigger count or the
sample count is greater than 1. If more than 512 measurements are made,
only the last 512 readings are stored. Use the
READ? command for more
than 512 readings since readings are immediately put into the output buffer
and retrieved with an I/O construct you supply. The measurement process
stops when the output buffer fills if readings are not retrieved fast enough.