56 HP E1312A/E1412A Multimeter Application Information Chapter 2
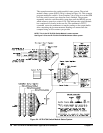
MEASURE4
Source Code File
Maximizing Accuracy (most accurate resolution, longer integration time)
*RST
Reset the multimeter.
CONF:VOLT:DC AUTO,MIN
Configure for dc volts, autorange, minimum
resolution (longest integration time).
TRIG:SOUR EXT
Set trigger source to external.
TRIG:COUN 2
Set trigger count to 2.
SAMP:COUN 10
Set sample count to 10.
READ?
Initiate measurements putting them directly
into output buffer; retrieve them with the
computer.
enter statement
Enter reading into computer.
Comments • The CONFigure command configures the multimeter for the function
specified. This
CONFigure command specifies autorange and
minimum resolution (the smallest resolution value which is the best
resolution). It does not initiate the measurement.
• Specifying a small value for resolution provides the most accurate
measurements. This will increase the integration time (NPLCs) and
therefore require more time for the measurements.
• Trigger source (TRIG:SOUR) is set for an external trigger. A trigger
count (
TRIG:COUN) of 2 is set; the multimeter will accept two
external triggers.
• The sample count (SAMP:COUN) is set for 10 samples per external
trigger.
• The READ? command puts the multimeter in the wait-for-trigger state.
When the first external trigger is received, the measurement process
begins. This will cause the multimeter to make 10 measurements for
the first external trigger, go to the wait-for-trigger state and take 10
measurements for the second external trigger when received.
• The readings are stored in the output buffer and you must provide the
I/O construct to retrieve the readings and enter them into the computer.
• This example uses the READ? command. Measurements are initiated
with the
READ? command which puts the multimeter in the wait-for-
trigger state. Measurement occurs when the trigger arrives and readings
are subsequently stored directly in the output buffer and must be
retrieved by the computer with an I/O construct you supply. An
alternative way of initiating measurements is to use the
INITiate
command as done in the previous example. Measurements are made and
stored in the multimeter’s internal memory and must be retrieved using
the
FETCh? command which transfers the readings to the output buffer.
You must be careful when using the
INITiate and FETCh? commands.
Internal memory stores a maximum of 512 readings; the oldest readings
exceeding 512 are lost.