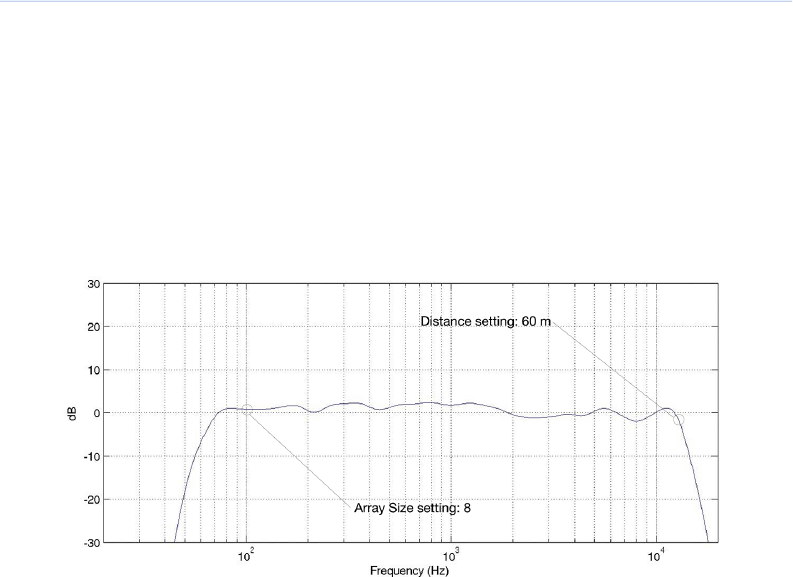
shown in Figure C.3: “Corrected Eight MILO Array at 60M” (p. 153), by performing these functions:
■
High-frequency attenuation is corrected by setting the Natural Environment for
Atmospheric Correction to actual conditions: Temperature of 20° C, Humidity at 50%,
Altitude below 800m, and (on the channel Output Processing pages) Atmospheric
Correction Distance at 60 meters.
■
Low and low-mid frequency build-up is corrected by setting the M Series Array Correction
to reflect the actual type and number of loudspeakers: Array Type MILO and Array Size
8.
Figure C.3. Corrected Eight MILO Array at 60M
The response in this example could be the ideal response or the perfect starting point for
achieving other equalization curves.
High-Frequency Response Curves
Reducing the Atmospheric Correction Distance parameter changes the amount of atmospheric
correction, making it possible to produce different responses in the high frequency range.
Figure C.4: “Corrected Eight MILO Array at Various Distances” (p. 154) shows the response of
the example MILO array (already compensated in the low frequencies) with distance settings
at 60, 40, and 20 meters.
153
APPENDIX C
USER-DEFINED EQUALIZATION CURVES WITH M SERIES ARRAY AND
ATMOSPHERIC CORRECTION
