C-8 APPENDIX C: ATM AND VLAN MANAGEMENT BASICS
ATM-based VLANs
When the enabling technology is ATM, the VLAN is referred to as an
ATM-based VLAN. An ATM-based VLAN is built around an ATM network
structure called an Emulated LAN.
LAN Emulation The main objective of the LAN Emulation (LE) is to
enable existing applications to access an ATM network via protocol stacks
as if they were operating over traditional LANs. LE enables data
networking protocol software to benefit from high-speed ATM
networking without modification. Legacy end stations can use LE to
connect to other legacy systems, as well as to ATM-attached servers,
routers, switches and other networking devices. LE is completely
independent of upper-layer protocols, services, and applications.
Because LE is implemented in edge devices and end systems, it is
completely transparent to the ATM network and to legacy LAN devices.
LE masks the connection setup and handshaking functions required by
the ATM switch. In addition, it maps the MAC address-based networking
protocols into ATM virtual channels. The ATM network appears to
function like a connectionless LAN.
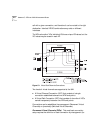
LAN Emulation Components An Emulated LAN (ELAN) is composed
of a set of LAN Emulation Clients (LECs) and a single LAN Emulation
Service, consisting of LAN Emulation Server (LES), and Broadcast and
Unknown Server (BUS). In addition there is also a LAN Emulation
Configuration Server (LECS) that services all the Emulated LANs that exist
in the ATM network. Refer to Figure C-3.
One or more Emulated LANs can run on the same ATM network. Each
Emulated LAN is independent of the others and there is no direct
communication across Emulated LAN boundaries.
An ATM-based VLAN is simply an ELAN together with all Ethernet LANs
attached to the LECs of the ELAN.
LAN Emulation
Client (LEC)
The LAN Emulation Client is the entity in end systems (e.g., a Super Stack
II Switch 2700 module) which represents the member Ethernet LANs and
performs data forwarding, address resolution, and other control
functions. If the LEC is attached to an Ethernet bridge, rather than
directly to a Ethernet LAN, the LEC acts as a proxy to MAC addresses of
Ethernet LANs attached to the bridge. Also provided is a MAC-level