An Introduction to ATM and VLAN Management Basics C-11
the configuration is such, the network manager should ensure that IP
connectivity to the device is not affected by VLAN moves.
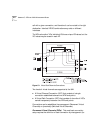
The Default VLAN When an ATM edge device is initialized, a single
VLAN called the default VLAN is created automatically and all ports of
the device are assigned to it.
In the SuperStack II Switch 2700 module, the Admin VLAN is also used as
the Default VLAN when the SuperStack II Switch 2700 is first initialized.
All ports are initially assigned to the Admin VLAN to ensure that they
have connectivity to the network. The Network Administrator can then
move the ports to another VLAN. At least one port must remain in the
Admin VLAN if the device is to be reached for management purposes.
Non-ATM VLANs
VLANs can be created on non-ATM based switches by using either
packet-tagging or packet-filtering (policy-based) techniques. The
Superstack II Switch 1000/3000 uses the packet-tagging mechanism.
VLAN management in the Superstack II Switch 1000/3000 system is
supported by a “VLAN Server” - a database which stores and retrieves
information about station VLAN membership.
The CoreBuilder 2500/6000 uses packet-filtering. The CoreBuilder
2500/6000 can link up with Emulated LANs to create policy-based Virtual
LANs “over ATM.” The following sections describe both these VLAN
mechanisms.
Tag-based VLANs
In tag-based VLANS, as employed by the Superstack II Switch 1000/3000,
ports can be grouped across multiple switches to form a single broadcast
domain. Packets within each VLAN group are tagged with a unique
identifier. The switches segment the traffic using these identifiers. Each
Superstack II Switch 1000 can support up to 16 VLANs and you can have
more than 16 VLANs in your entire network by connecting the 16 Switch
VLANs to other VLANS using a router.
Virtual LAN Trunk VLANs can be defined in a single switch unit or can span several Switch
units. When a VLAN spans two switch units, they are connected using
backbone ports. The tagging method, described below, makes it possible
for a single backbone port to carry the traffic for all VLANs defined in a
switch. In that case, the backbone port is referred to as a Virtual LAN