HRB1684301-01 135
Chapter 16 Power, energy and power factor
This section describes how the meter interprets and calculates power and power factor.
Power (PQS)
A typical AC electrical system load has both resistive and reactive (inductive or
capacitive) components. Resistive loads consume real power (P) and reactive loads
consume reactive power (Q).
Apparent power (S) is the vector sum of real power (P) and reactive power (Q):
Real power is measured in watts (W or kW), reactive power is measured in vars (VAR
or kVAR) and apparent power is measured in volt-amps (VA or kVA).
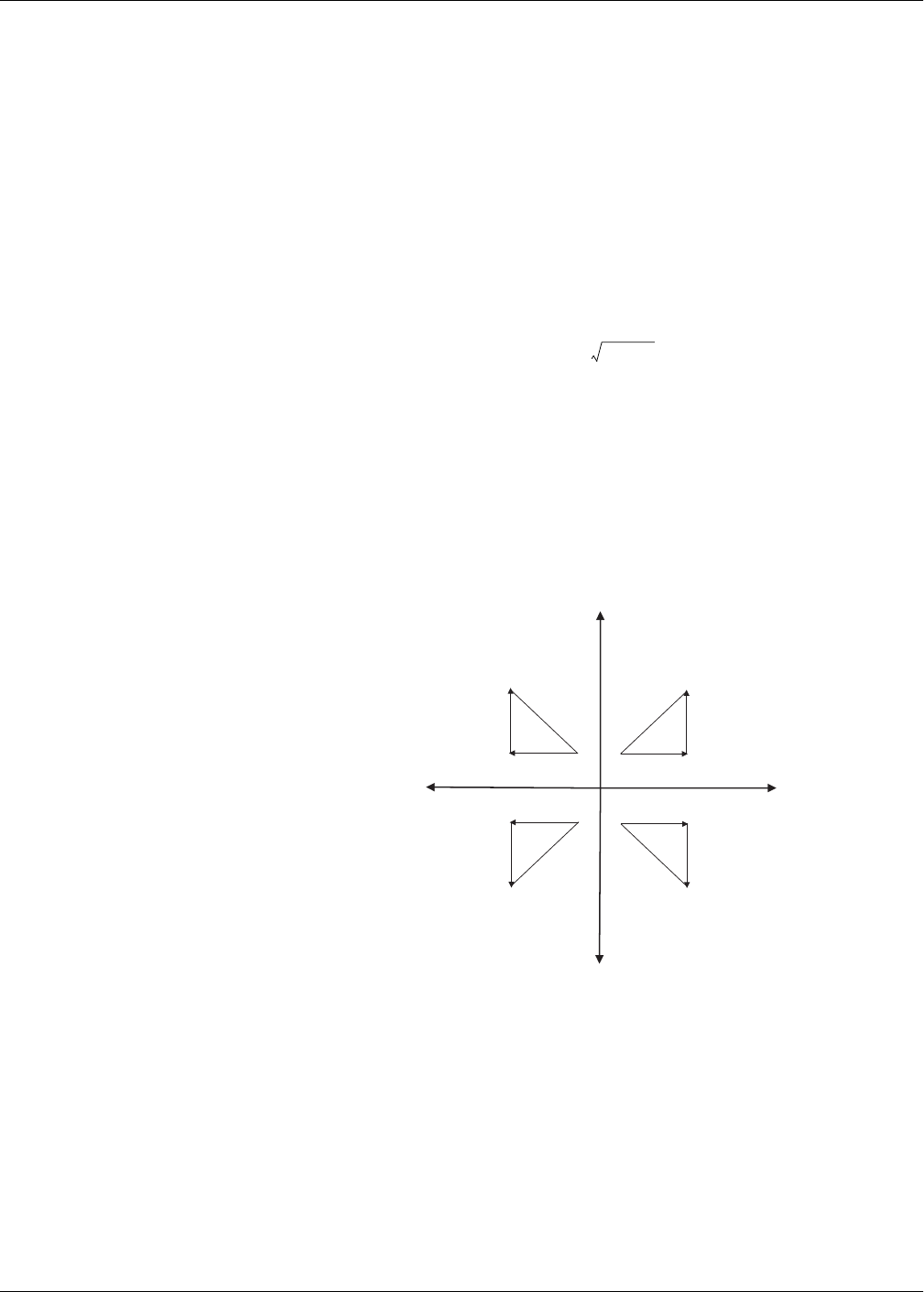
Power and the PQ coordinate system
The meter uses the values of real power (P) and reactive power (Q) on the
PQ coordinate system to calculate apparent power.
Power flow
Positive power flow P(+) and Q(+) means power is flowing from the power source
towards the load. Negative power flow P(-) and Q(-) means power is flowing from the
load towards the power source.
SP
2
Q
2
+=
PQ coordinate system
+Q
(+kVAR)
-P
(-kW)
-Q
(-kVAR)
+P
(+kW)
P (+)
S
P (-)
S
P (+)
S
P (-)
S
Q (-)Q (-)
Q (+) Q (+)
Quadrant 3 Quadrant 4
Quadrant 1
Quadrant 2