341
Measurement of main circuit voltages,
currents and powers
6
PRECAUTIONS FOR MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION
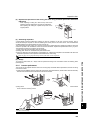
Measuring Points and Instruments
*1 Use an FFT to measure the output voltage accurately. A tester or general measuring instrument cannot measure accurately.
*2 When the carrier frequency exceeds 5kHz, do not use this instrument since using it may increase eddy-current losses produced in metal parts
inside the instrument, leading to burnout. If the wiring length between the inverter and motor is long, the instrument and CT may generate
heat due to line-to-line leakage current.
*3 When the setting of Pr. 195 ABC1 terminal function selection is positive logic
*4 A digital power meter (designed for inverter) can also be used to measure.
Item Measuring Point Measuring Instrument Remarks (Reference Measured Value)
Power supply voltage
V
1
Across R/L1 and S/L2,
S/L2 and T/L3,
T/L3 and R/L1
Moving-iron type AC
voltmeter
*4
Commercial power supply
Within permissible AC voltage fluctuation
Refer to page 346.
Power supply side
current
I
1
R/L1, S/L2, and T/L3
line currents
Moving-iron type AC
ammeter
*4
Power supply side
power
P1
R/L1, S/L2, T/L3 and
R/L1
and
S/L2,
S/L2
and
T/L3,
T/L3
and
R/L1
Digital power meter
(designed for inverter) or
e
lectrodynamic type
single-phase wattmeter
P1=W11+W12+W13 (3-wattmeter method)
Power supply side
power factor
Pf
1
Calculate after measuring power supply voltage, power supply side current and power supply side power.
Output side voltage
V
2
Across U and V,
V and W
and W and U
Rectifier type AC voltage
meter
*1 *4
(Moving-iron type cannot
measure)
Difference between the phases is within ±1% of the
maximum output voltage.
Output side current
I
2
U, V and W line
currents
Moving-iron type AC
ammeter
*2 *4
Difference between the phases is 10% or lower of the
rated inverter current.
Output side power
P
2
U, V, W and
U and V,
V and W
Digital power meter
(designed for inverter) or
e
lectrodynamic type
single-phase wattmeter
P2 = W21 + W22
2-wattmeter method (or 3-wattmeter method)
Output side power
factor
Pf2
Calculate in similar manner to power supply side power factor.
Converter output Across P/+ and N/−
Moving-coil type (such
as tester)
Inverter LED display is lit. 1.35
× V1
Frequency setting
signal
Across 2 and 5
Across 4(+) and 5
Moving-coil type
(Tester and such may be
used)
(Internal resistance:
50kΩ or larger)
0 to 10VDC, 4 to 20mA
"5" is
common
Across 1(+) and 5 0 to ±5VDC, 0 to ±10VDC
Frequency setting
power supply
Across 10 (+) and 5 5.2VDC
Across 10E(+) and 5 10VDC
Frequency meter
signal
Across AM(+) and 5
Approximately 10VDC at maximum frequency
(without frequency meter)
Across FM(+) and SD
Approximately 5VDC at maximum frequency
(without frequency meter)
Pulse width T1:
Adjusted by C0 (Pr. 900)
Pulse cycle T2: Set by Pr. 55
(Valid for frequency monitoring only)
"SD" is
common
Start signal
Select signal
Across SD and the
following:
STF, STR, RH, RM,
RL, JOG, RT, AU,
STOP, CS (+)
When open
20 to 30VDC
ON voltage: 1V or less
Reset
Across RES (+)
and
SD
Output stop
Across MRS (+)
and
SD
Fault signal
Across A1 and C1
Across B1 and C1
Moving-coil type
(such as tester)
Electric continuity check
*3
<Normal> <Fault>
Across A1 and C1 Discontinuity Continuity
Across B1 and C1 Continuity Discontinuity
Pf1 = ————— × 100%
P
1
3 V1 × I1
Pf2 = ————— × 100%
P
2
3 V2 × I2
8VDC
T1
T2