Intel® Server Board SE7501WV2 TPS BIOS
Revision 1.0
Intel reference number C25653-001
133
• User binary code must be relocatable. It will be located within the first Megabyte. The
user binary code should not make any assumptions about the value of the code segment.
• User binary code will always be executed from RAM and never from flash.
• The code in user binary should not hook critical interrupts, should not reprogram the
chipset and should not take any action that affects the correct functioning of the system
BIOS.
The BIOS copies the user binary into system memory before the first scan point. If the user
binary reports that it does not contain runtime code, it is located in conventional memory (0 -
640 KB).
Reporting that the user binary is POST has only the advantage that it does not use up limited
option ROM space, and more option ROMs can be fitted. If user binary code is required at run-
time, it is copied to option ROM space. At each scan-point during POST, the system BIOS
determines if this scan-point has a corresponding user binary entry point to which it transfers
control.
To determine this, the bitmap at byte 4 of the header is tested against the current mask bit that
has been determined / defined by the scan point. If the bitmap has the appropriate bit set, the
mask is placed in AL and execution is passed to the address computed by (ADR(Byte 5)+5*scan
sequence #).
During execution, the user binary may access 11 bytes of Extended BIOS Data Area RAM
(EBDA). The segment of the EBDA can be found at address 40:0e. Offset 18 to offset 21h is
available for the user binary. The BIOS also reserves eight CMOS bits for the user binary.
These bits are in a non-checksummed region of CMOS with default values of zero, and will
always be located in the first bank of CMOS. These bits are contiguous, but are not in a fixed
location. Upon entry into the user binary, DX contains a ‘token’ that points to the reserved bits.
This token has the following format:
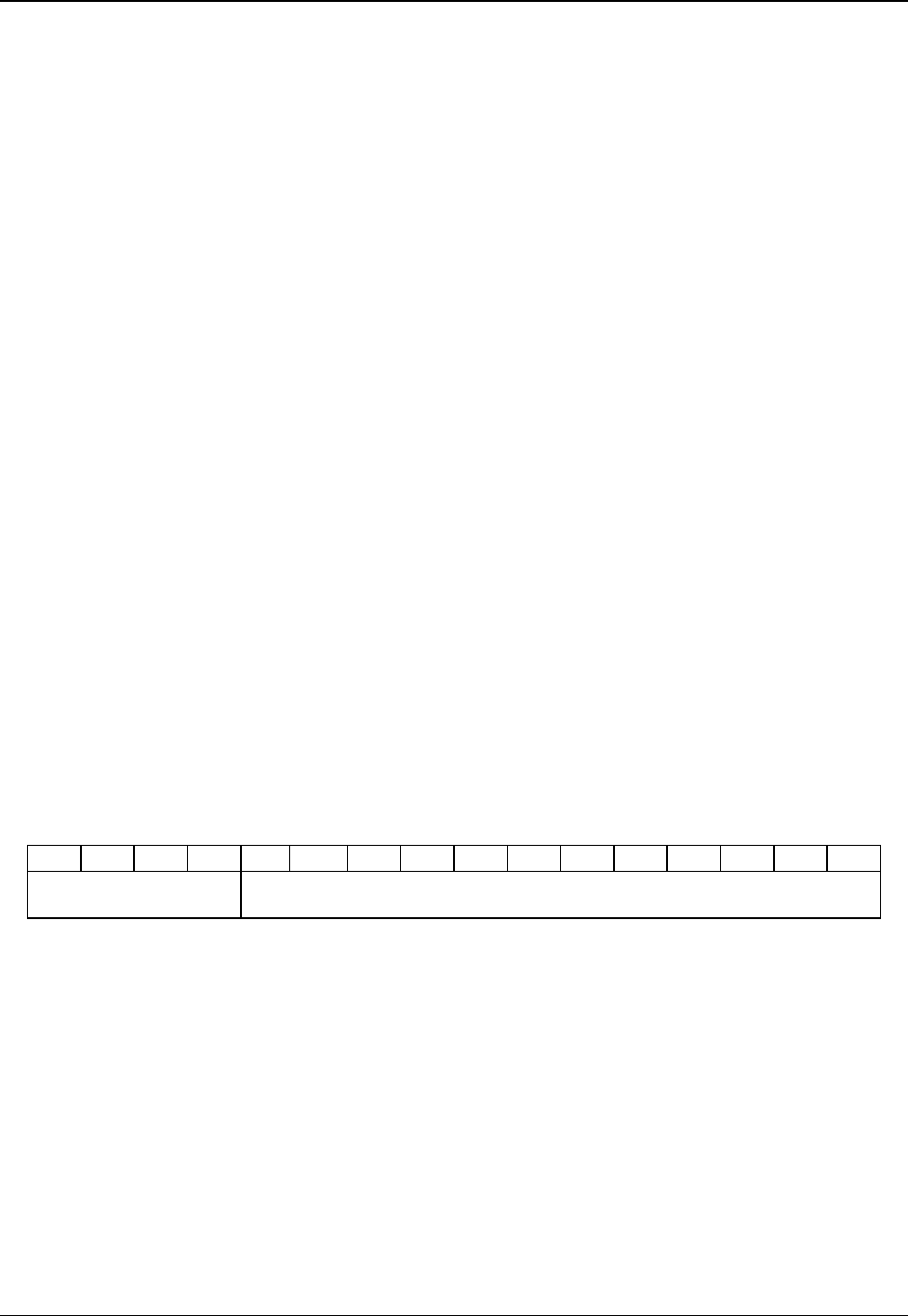
MSB LSB
15 12 11 0
# of bits
available –1
Bit offset from start of CMOS of first bit
The most significant 4 bits are equal to the number of CMOS bits available, minus 1. This field is
equal to 7 since 8 CMOS bits are available. The 12 least significant bits define the position of
the CMOS bit in RTC. This is a bit address, not a byte address. The CMOS byte location is
1/8th of the 12-bit number, and the remainder is the starting bit position within that byte. For
example, if the 12-bit number is 0109h, user binary can use bit 1 of CMOS byte 0108h/8 or
021h.