179
Measurement of main circuit voltages,
currents and powers
6
PRECAUTIONS FOR MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION
6.2.1 Measurement of powers
Use digital power meters (for inverter) for the both of inverter input and output side. Alternatively, measure using
electrodynamic type single-phase wattmeters for the both of inverter input and output side in two-wattmeter or
three- wattmeter method. As the current is liable to be imbalanced especially in the input side, it is recommended to
use the three-wattmeter method.
Examples of measured value differences produced by different measuring meters are shown below.
An error will be produced by difference between measuring instruments, e.g. power calculation type and two- or
three-wattmeter type three-phase wattmeter. When a CT is used in the current measuring side or when the meter
contains a PT on the voltage measurement side, an error will also be produced due to the frequency characteristics
of the CT and PT.
6.2.2 Measurement of voltages and use of PT
(1) Inverter input side
As the input side voltage has a sine wave and it is extremely small in distortion, accurate measurement can be
made with an ordinary AC meter.
(2) Inverter output side
Since the output side voltage has a PWM-controlled rectangular wave, always use a rectifier type voltmeter. A
needle type tester can not be used to measure the output side voltage as it indicates a value much greater than the
actual value. A moving-iron type meter indicates an effective value which includes harmonics and therefore the
value is larger than that of the fundamental wave. The value monitored on the operation panel is the inverter
controlled voltage itself. Hence, that value is accurate and it is recommended to monitor values (provide analog
output) using the operation panel.
(3) PT
No PT can be used in the output side of the inverter. Use a direct-reading meter. (A PT can be used in the input side
of the inverter.)
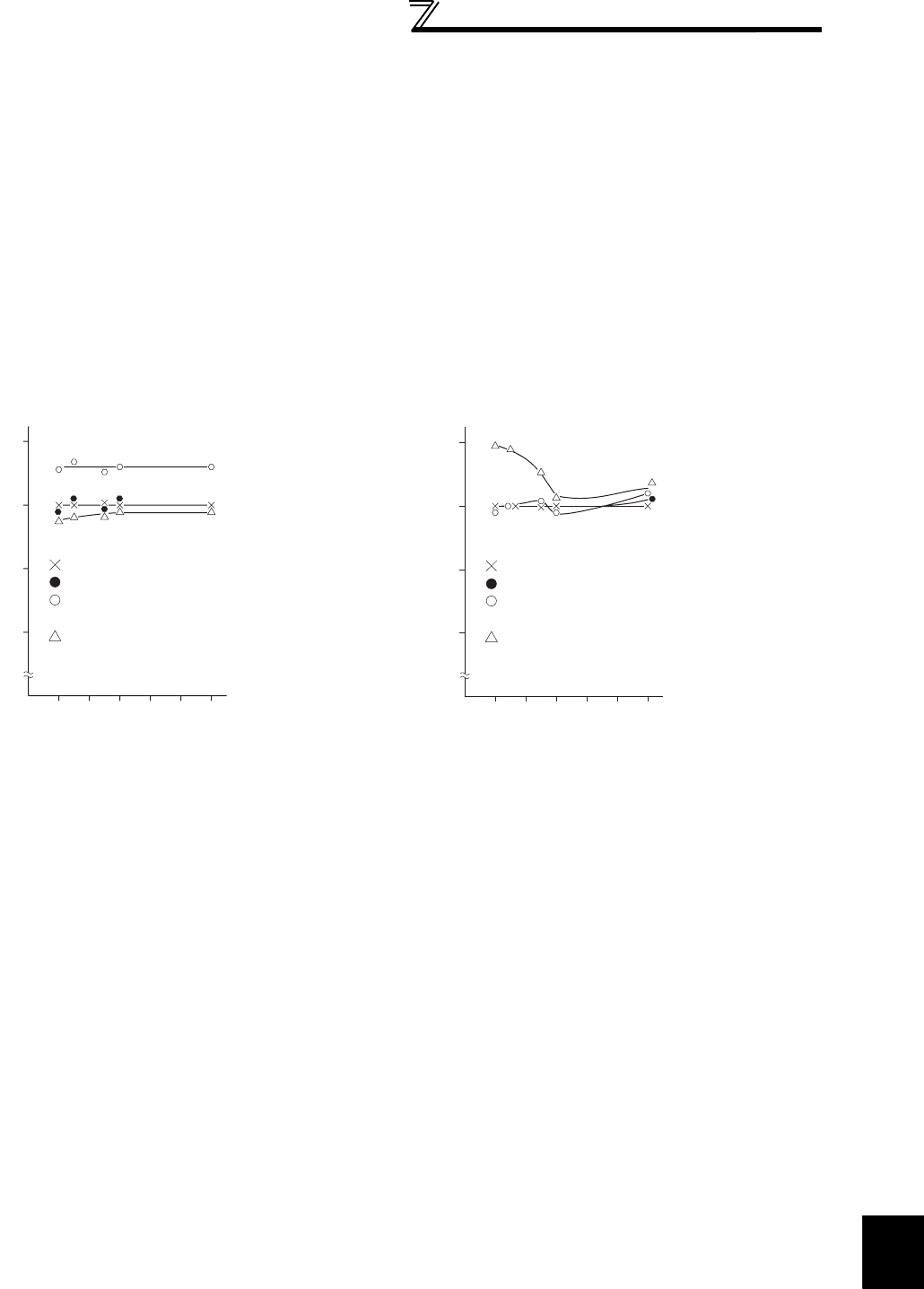
[Measurement conditions]
Constant-torque (100%) load, constant-power at 60Hz
or more.
3.7kW, 4-pole motor, value indicated in 3-wattmeter
method is 100%.
[Measurement conditions]
Constant-torque (100%) load, constant-power at 60Hz
or more.
3.7kW, 4-pole motor, value indicated in 3-wattmeter
method is 100%.
Example of measuring inverter input power Example of measuring inverter output power
3-wattmeter method (Electro-dynamometer type)
2-wattmeter method (Electro-dynamometer type)
Clip AC power meter
(For balanced three-phase load)
Clamp-on wattmeter
(Hall device power arithmetic type)
0 20 40 60 80 100120Hz
60
80
100
120
%
3-wattmeter method (Electro-dynamometer type)
2-wattmeter method (Electro-dynamometer type)
Clip AC power meter
(For balanced three-phase load)
Clamp-on wattmeter
(Hall device power arithmetic type)
0 20 40 60 80 100120Hz
60
80
100
120
%


















