12
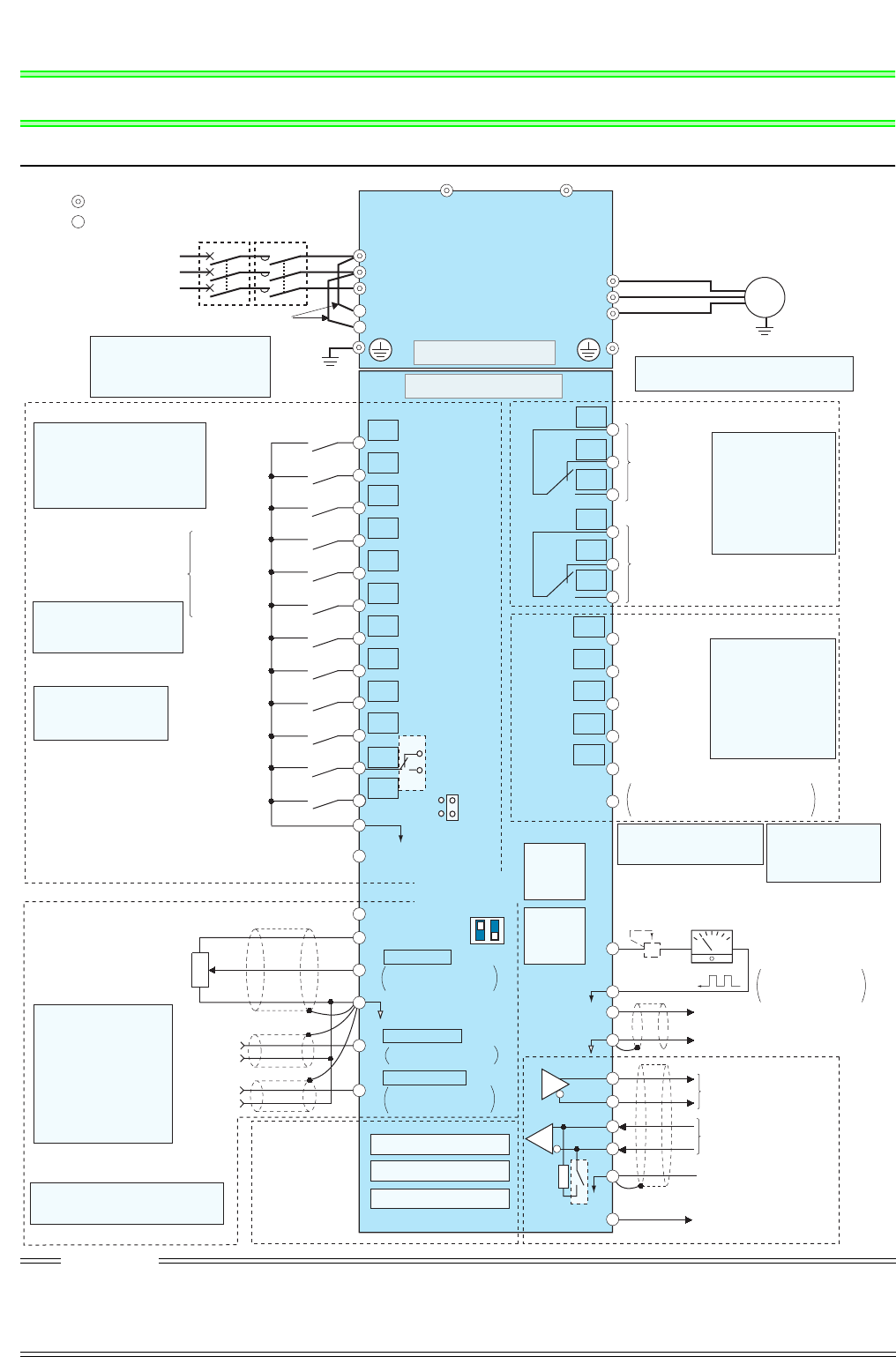
Terminal connection diagram
2 WIRING
2.1 Terminal connection diagram
CAUTION
· To prevent a malfunction due to noise, keep the signal cables more than 10cm away from the power cables. Also separate the main circuit wire
of the input side and the output side.
· After wiring, wire offcuts must not be left in the inverter.
Wire offcuts can cause an alarm, failure or malfunction. Always keep the inverter clean.
When drilling mounting holes in an enclosure etc., take care not to allow chips and other foreign matter to enter the inverter.
· Set the voltage/current input switch correctly. Different setting may cause a fault, failure or malfunction.
R/L1
S/L2
T/L3
R1/L11
S1/L21
PC
10E(+10V)
10(+5V)
2
(Analog common)
2
3
1
1
4
C1
B1
A1
U
V
W
0 to
±
10VDC
0 to 5VDC
0 to 10VDC
MC
Main circuit
Control circuit
C2
B2
A2
IM
0 to 20mADC
AU
PTC
TXD+
TXD-
RXD+
RXD-
SG
GND
SINK
SOURCE
*3
*2
*4
STF
STR
STOP
RH
RM
RL
JOG
RT
MRS
RES
AU
CS
SD
RUN
SU
IPF
OL
FU
SE
(+)
(-)
5
VCC
(+)
(-)
5V
*1
Earth (Ground)
N/-P/+
*2. JOG terminal can be used
as pulse train input terminal.
Use Pr. 291 to select
JOG/pulse.
Main circuit terminal
Control circuit terminal
Three-phase AC
power supply
MCCB
Jumper
Earth
(Ground)
selectable
selectable
selectable
0 to ±5VDC
*4
4 to 20mADC
0 to 5VDC
0 to 10VDC
*4
Option connector 1
Option connector 2
Option connector 3
Connector
for plug-in option
connection
Frequency setting signal (Analog)
Frequency setting
potentiometer
1/2W1k
Ω
*5
Control input signals (No voltage input allowed)
Forward
rotation
start
Reverse
rotation
start
Start self-
holding selection
Terminal functions vary with
the input terminal
assignment (Pr. 178 to Pr. 189)
Middle
speed
High speed
Low speed
Multi-speed
selection
Jog operation
Second function selection
Output stop
Reset
Terminal 4 input selection
(Current input selection)
Selection of automatic restart
after instantaneous
power failure
USB
connector
PU
connector
Terminating
resistor
Data reception
Data transmission
RS-485 terminals
Open collector output common
Sink
/source common
Frequency detection
Running
Up to frequency
Instantaneous
power failure
Overload
Terminal functions
vary with the output
terminal assignment
(Pr. 190 to Pr. 194)
Open collector output
(Permissible load
current 100mA)
Relay output 2
Relay output 1
(Fault output)
Terminal functions
vary with the output
terminal assignment
(Pr. 195, Pr. 196)
Relay output
Motor
*3. AU terminal can be
used as PTC input
terminal.
*1. To supply power to the
control circuit separately,
remove the jumper across
R1/L11 and S1/L21.
*
7. It is not necessary when
calibrating the indicator
from the operation panel.
*5
. It is recommended to use 2W1kΩ
when the frequency setting signal
is changed frequently.
(Initial value)
(Initial value)
(Initial value)
ON
4
2
OFF
Voltage/current
input switch
*4
Auxiliary
input
Terminal
4 input
(Current
input)
*
4.
Terminal input specifications
can be changed by analog
input specifications
switchover (Pr. 73, Pr. 267).
Set the voltage/current input
switch in the OFF position to
select voltage input (0 to 5V/0
to10V) and ON to select
current input (4 to 20mA).
Sink logic
*6. Do not connect any options to P/+ and
N/-.
FM
SD
+
-
AM
5
*8
*8. FM terminal can be
used for pulse train
output of open
collector output
using Pr.291.
(+)
(-)
(0 to 10VDC)
Analog signal output
Moving-coil type
1mA full-scale
(Frequency meter, etc.)
Indicator
Calibration
resistor
*
7
24VDC power supply
(Common for external power supply transistor)
Contact input common
*6 *6
(Refer to Chapter 4 of the Instruction
Manual (Applied))
(Refer to Chapter 4 of the
Instruction Manual
(Applied))
(Refer to Chapter 4 of the
Instruction Manual
(Applied))
(Refer to Chapter 4 of the
Instruction Manual (Applied))