352
Communication operation and setting
Function diagnosis (H08 or 08)
A communication check can be made since the query message sent is returned unchanged as a response
message (function of subfunction code H00).
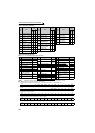
Subfunction code H00 (Return Query Data)
Query Message
Normal Response (Response message)
⋅ Query message setting
⋅ Description of normal response
1) to 4) (including CRC check) of the normal response are the same as those of the query message.
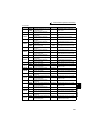
Write multiple holding register data (H10 or 16)
You can write data to multiple holding registers.
Query message
Normal Response (Response message)
⋅ Query message setting
1) Slave Address 2) Function 3) Subfunction 4) Date CRC Check
(8 bits)
H08
(8 bits)
H00
(8 bits)
H00
(8 bits)
H
(8 bits)
L
(8 bits)
L
(8 bits)
H
(8 bits)
1) Slave Address 2) Function 3) Subfunction 4) Date CRC Check
(8 bits)
H08
(8 bits)
H00
(8 bits)
H00
(8 bits)
H
(8 bits)
L
(8 bits)
L
(8 bits)
H
(8 bits)
Message Setting Description
1)Slave Address
Set the address to which the message will be sent. Broadcast
communication cannot be made (0 is invalid).
2)Function
Set H08.
3)Subfunction
Set H0000.
4)Data
Any data can be set if it is 2 bytes long. The setting range is H0000
to HFFFF.
CAUTION
For broadcast communication, no response is returned in reply to a query. Therefore, the next query must be made when
the inverter processing time has elapsed after the previous query.
1)
Slave
Address
2)
Function
3)
Starting Address
4) No. of
Registers
5)
ByteCount
6) Data CRC Check
(8 bits)
H10
(8 bits)
H
(8 bits)
L
(8 bits)
H
(8 bits)
L
(8 bits)
(8 bits)
H
(8 bits)
L
(8 bits)
...
(n
×
2
×
8 bits)
L
(8 bits)
H
(8 bits)
1) Slave Address 2) Function
3) Starting Address
4) No. of Registers CRC Check
(8 bits)
H10
(8 bits)
H
(8 bits)
L
(8 bits)
H
(8 bits)
L
(8 bits)
L
(8 bits)
H
(8 bits)
Message Setting Description
1)Slave Address
Set the address to which the message will be sent. Setting of address 0
enables broadcast communication.
2)Function Set H10.
3)Starting Address
Set the address where holding register data write will be started.
Starting address = starting register address (decimal) − 40001
For example, setting of the starting address 0001 reads the data of the
holding register 40002.
4)No. of Points
Set the number of holding registers where data will be written. The number of
registers where data can be written is a maximum of 125.
5)Byte Count
The setting range is H02 to HFA (2 to 250).
Set a value twice greater than the value specified at 4).
6)Data
Set the data specified by the number specified at 4). The written data are set
in order of Hi byte and Lo byte, and arranged in order of the starting address
data, starting address + 1 data, starting address + 2 data ...