29
Control circuit specifications
2
WIRING
4)Sink logic and source logic
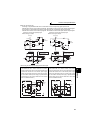
⋅ In sink logic, a signal switches ON when a current flows from the corresponding signal input terminal.
Terminal SD is common to the contact input signals. Terminal SE is common to the open collector output signals.
⋅ In source logic, a signal switches ON when a current flows into the corresponding signal input terminal.
Terminal PC is common to the contact input signals. Terminal SE is common to the open collector output signals.
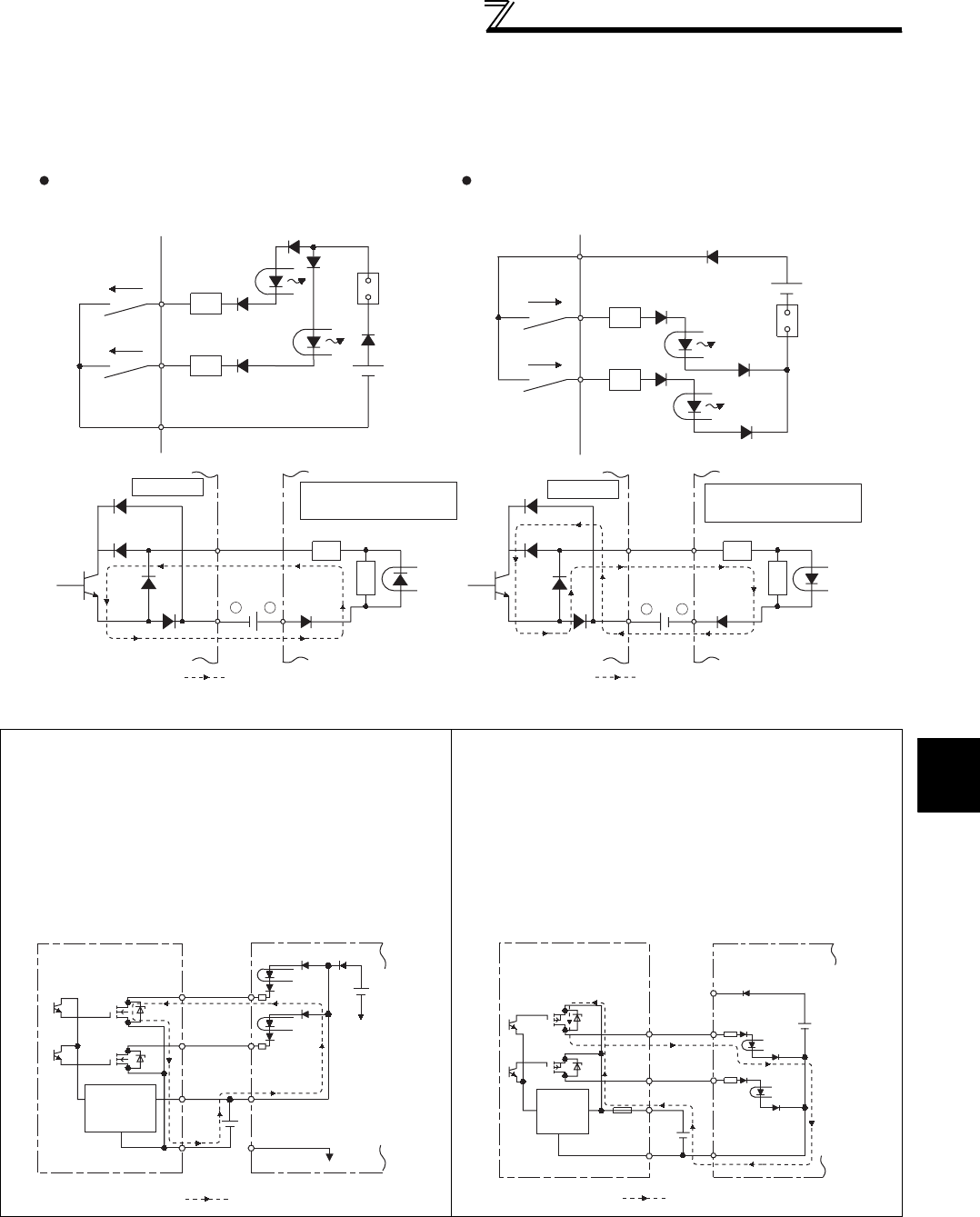
• When using an external power supply for transistor output
Sink logic type
Use terminal PC as a common terminal, and perform
wiring as shown below. (Do not connect terminal SD of the
inverter with terminal 0V of the external power supply.
When using terminals PC-SD as a 24VDC power supply,
do not install an external power supply in parallel with the
inverter. Doing so may cause a malfunction in the inverter
due to undesirable currents.)
Source logic type
Use terminal SD as a common terminal, and perform
wiring as shown below. (Do not connect terminal PC of the
inverter with terminal +24V of the external power supply.
When using terminals PC-SD as a 24VDC power supply,
do not install an external power supply in parallel with the
inverter. Doing so may cause a malfunction in the inverter
due to undesirable currents.)
Current
PC
STF
R
STR
R
Source logic
Source
connecto
r
Current
SD
STF
R
STR
R
Sink
connector
Sink logic
Current flow concerning the input/output signal
when sink logic is selected
Current flow concerning the input/output signal
when source logic is selected
DC input (source type)
<Example: QX80>
24VDC
RUN
SE
TB1
TB18
R
Inverter
R
Current flow
+
-
+
-
DC input (sink type)
<Example: QX40>
Inverter
24VDC
RUN
SE
TB1
TB17
R
R
Current flow
QY40P type transistor
output unit
TB1
TB2
TB17
TB18
24VDC
SD
PC
STR
STF
Inverter
24VDC
(SD)
Current flow
Constant
voltage
circuit
QY80 type transistor
output unit
Constant
voltage
circuit
PC
TB1
TB2
TB17
Fuse
TB18
STF
STR
SD
Inverter
24VDC
(SD)
24VDC
Current flow