Development System Reference Guide www.xilinx.com 245
OFFSET Constraints
R
OFFSET OUT Path Details
The example path below passed the timing constraint by .533 ns. The slack equation shows
how the slack was calculated. Data delay increases the clock to out time and clock delay
also increases the clock to out time. The clock arrival time is also taken into account. In this
example the clock arrival time is 0.000 ns; therefore, it does not affect the slack.
If the clock edge occurs at a different time, this value is also added to the clock to out time.
If this example had the clock falling at 5.000 ns, 5.000 ns would be added to the slack
equation because the initial edge of the corresponding PERIOD constraint is HIGH.
Note:
The clock falling at 5.000 ns is determined by how the PERIOD constraint isdefined, for
example PERIOD 10 HIGH 5.
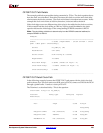
Example:
======================================================================
Slack: 0.533ns (requirement - (clock arrival + clock
path + data path + uncertainty))
Source: wr_addr[2] (FF)
Destination: efl (PAD)
Source Clock: wclk rising at 0.000ns
Requirement: 10.000ns
Data Path Delay: 9.952ns (Levels of Logic = 4)
Clock Path Delay: -0.485ns (Levels of Logic = 3)
Clock Uncertainty: 0.000ns
----------------------------------------------------------------------
OFFSET OUT Detail Clock Path
In the following example, because the OFFSET OUT path starts with the clock, the clock
path is shown first. The clock starts at an IOB, goes to a DCM, comes out CLK0 of the DCM
through a global buffer. It ends at a clock pin of a FF.
The Tdcmino is a calculated delay. This is the equation:
Clock Path: rclk_in to rd_addr[2]
Location Delay type Delay(ns) Logical
Resource(s)
-------------------------------------------------
A8.I Tiopi 0.825 rclk_in
read_ibufg
DCM_X1Y1.CLKIN net (fanout=1) 0.798 rclk_ibufg
DCM_X1Y1.CLK0 Tdcmino -4.290 read_dcm
BUFGMUX7P.I0 net (fanout=1) 0.852 rclk_dcm