286 www.xilinx.com Development System Reference Guide
Chapter 16: PROMGen
R
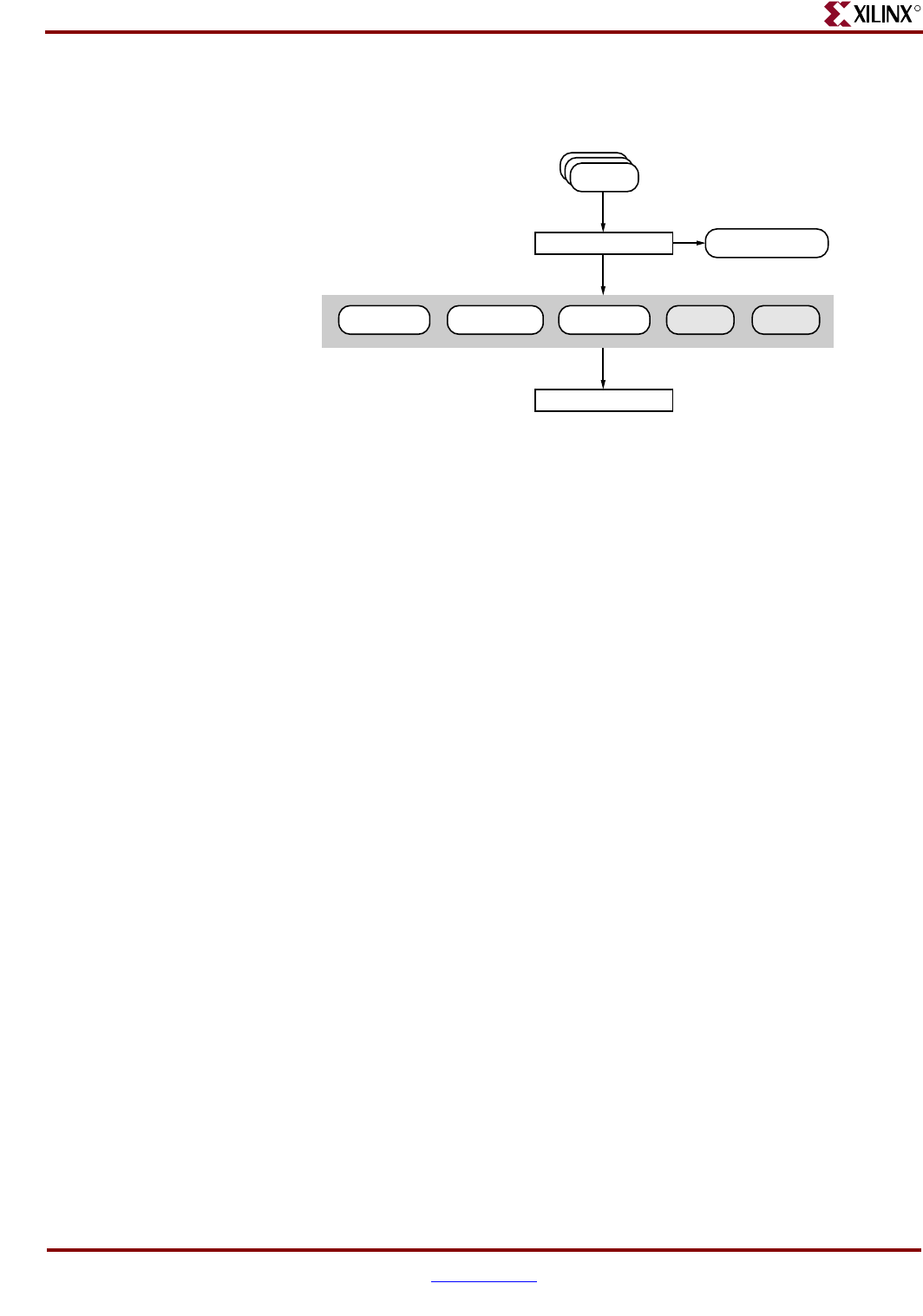
The following figure shows the inputs and the possible outputs of the PROMGen program:
There are two functionally equivalent versions of PROMGen. There is a stand-alone
version that you can access from an operating system prompt. There is also an interactive
version, called the PROM formatting wizard that you can access from inside Project
Navigator (see the iMPACT online help).
You can also use PROMGen to concatenate bitstream files to daisy-chain FPGAs.
Note:
If the destination PROM is one of the Xilinx Serial PROMs, you are using a Xilinx PROM
Programmer, and the FPGAs are not being daisy-chained, it is not necessary to make a PROM file.
PROMGen Syntax
To start PROMGen from the operating system prompt, use the following syntax:
promgen
[options]
options can be any number of the options listed in “PROMGen Options”. Separate multiple
options with spaces.
PROMGen Input Files
The input to PROMGEN consists of one or more BIT and RBT files. BIT files contain
configuration data for an FPGA design.
PROMGen Output Files
Output from PROMGEN consists of the following files:
• PROM files—The file or files containing the PROM configuration information.
Depending on the PROM file format your PROM programmer uses, you can output a
TEK, MCS, BIN, or EXO file. If you are using a microprocessor to configure your
devices, you can output a HEX file, which contains a hexadecimal representation of
the bitstream.
• PRM file—The PRM file is a PROM image file. It contains a memory map of the
output PROM file. The file has a .prm extension.
Figure 16-1: PROMGen
X9560
BIT
MCS
PROM File
PROMGen
Device Configuration
TEK
PROM File
HEX BIN
EXO
PROM File
PRM
Memory Map


















