Development System Reference Guide www.xilinx.com 329
NetGen Equivalence Checking Flow
R
–xon (Select Output Behavior for Timing Violations)
–xon {true|false}
The –xon option specifies the output behavior when timing violations occur on memory
elements. If you set this option to true, any memory elements that violate a setup time
trigger X on the outputs. If you set this option to false, the signal’s previous value is
retained. If you do not set this option, –xon true is run.
Note:
The –xon option should be avoided as much as possible. If there is an asynchronous path in
the design, the constraint ASYNC_REG should be used. Disabling the X propagation globally can
have detrimental results on the simulation and the timing simulation results may not match the
behavior seen in the hardware. Please see the Disabling X propagation section in the Synthesis and
Simulation Design Guide for more information.
NetGen Equivalence Checking Flow
This section describes the NetGen Equivalence Checking flow, which is used for formal
verification of FPGA designs. This flow creates a Verilog netlist and conformal or formality
assertion file for use with supported equivalence checking tools.
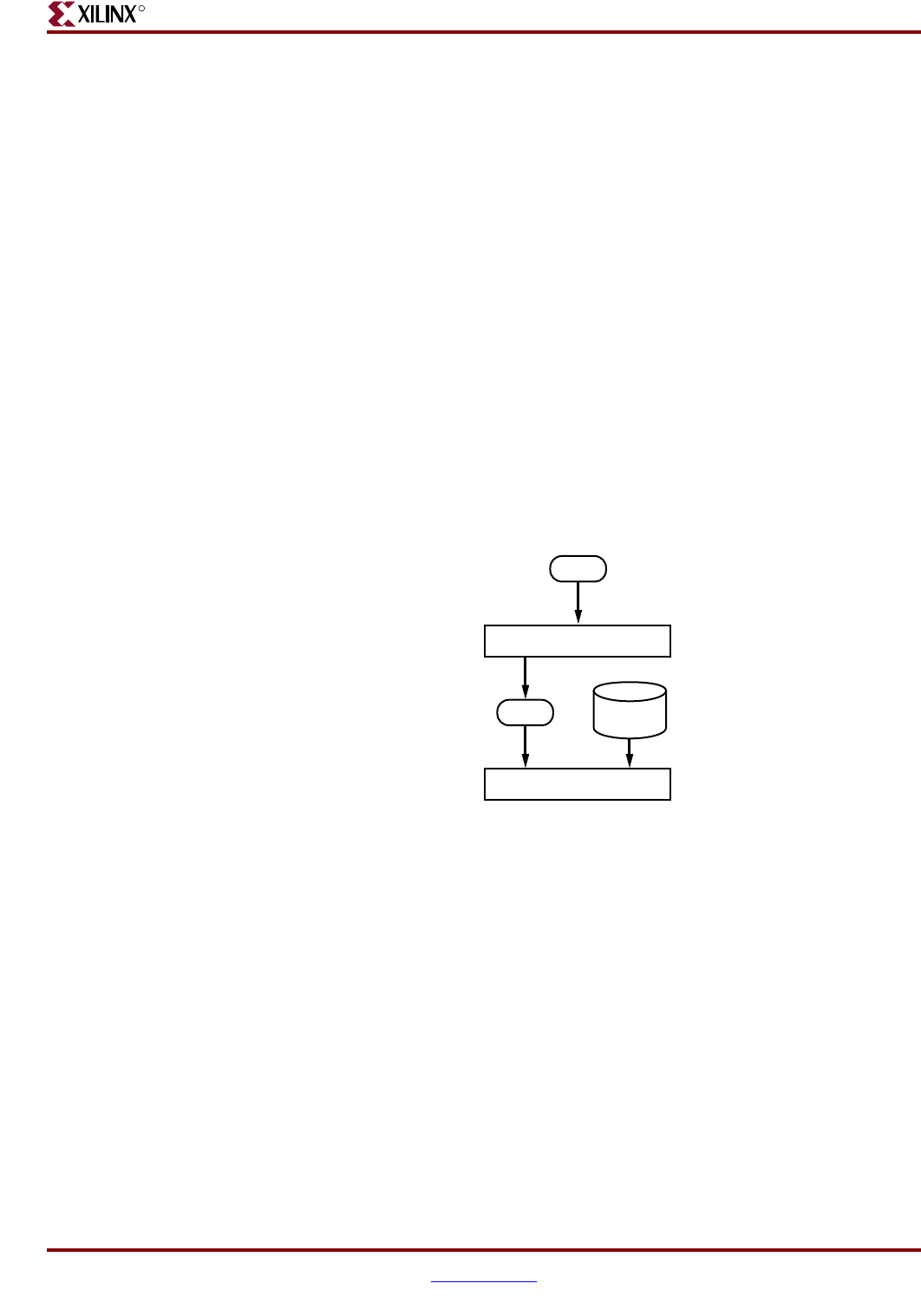
The figures below illustrate the NetGen Equivalence Checking flow for FPGA designs.
Figure 22-4: Post-NGDBuild Flow for FPGAs
X10035
NetGen
NGD
V
Formal Verification Tool
Formal
Library
